
How Does I2C for LCD Communication Work?
I2C lets a microcontroller talk to an LCD using only two wires: SDA (data) and SCL (clock).

I2C lets a microcontroller talk to an LCD using only two wires: SDA (data) and SCL (clock).

Capacitive touch screens detect fingers or conductive styluses through electrostatic field changes. Resistive touch screens register pressure from any input, like gloves or styluses, to connect flexible layers.

A level shifter safely connects a 3.3V LCD module to a 5V system by translating signal voltages to a range the display can handle.
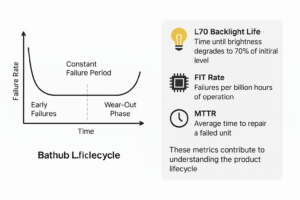
The typical Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) for commercial LCD modules ranges from 30,000 to 70,000 hours.
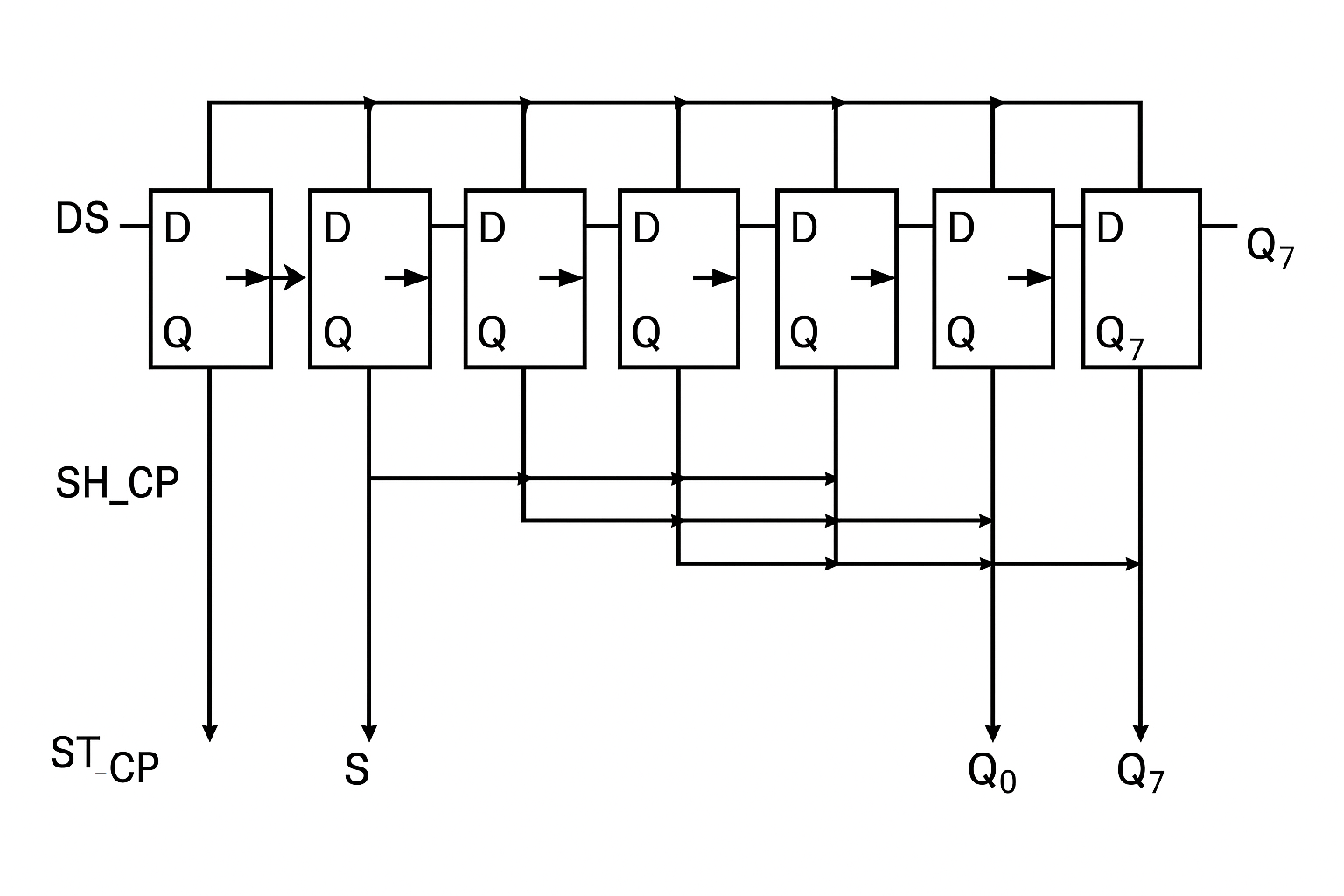
Parallel‑to‑serial conversion is needed because most microcontrollers do not have enough GPIO pins to support a full 8‑ or 16‑bit parallel LCD bus.

Signal timing controls data transfer in LCD displays. It ensures clear, stable images. Proper timing from datasheets prevents these artifacts.
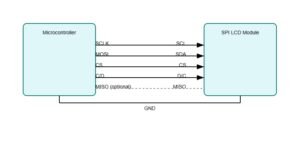
The master toggles SCLK to clock out bytes on MOSI and drives CS low to select the lcd spi interface. MISO can return status feedback when the display supports it.

In little-endian, the least significant byte (LSB) comes first. This difference affects how systems store and read data.
Embedded LCD System used for HAL Hardware abstraction layers (HALs) simplify LCD module integration across MCU platforms with better portability and faster development time. Custom display layers deliver higher performance for single-platform projects needing specific hardware features. Choose HALs for

The COB and COG LCD difference comes from where the control chip, or driver IC, is placed in the display structure.


Download our comprehensive catalog to explore 10,000+ LCD module options in detail:
0.42-10.11 inch TFT LCD
16×2-320×240 COB LCD
8×2-320×240 COG LCD