Optical bonding eliminates the air gap between display layers using transparent adhesive, while air bonding maintains an air gap with frame adhesive around the edges. The choice depends on your specific requirements for clarity, durability, and budget.
Let me share what I’ve learned from hundreds of projects about these two technologies. The decision you make here will impact everything from your end product’s performance to your customer satisfaction rates.
How Do Optical and Air Bonding Differ?
Understanding both methods starts with their fundamental mechanics. Let’s strip away marketing jargon to examine core technical differences.
Air bonding uses double-sided adhesive tape around the frame edges, maintaining an air gap between the touch panel and LCD module. Optical bonding applies transparent adhesive across the entire surface, eliminating the air gap completely.
Confusion often arises from vague terminology. Let’s define both processes clearly and explore their execution.
Optical bonding:
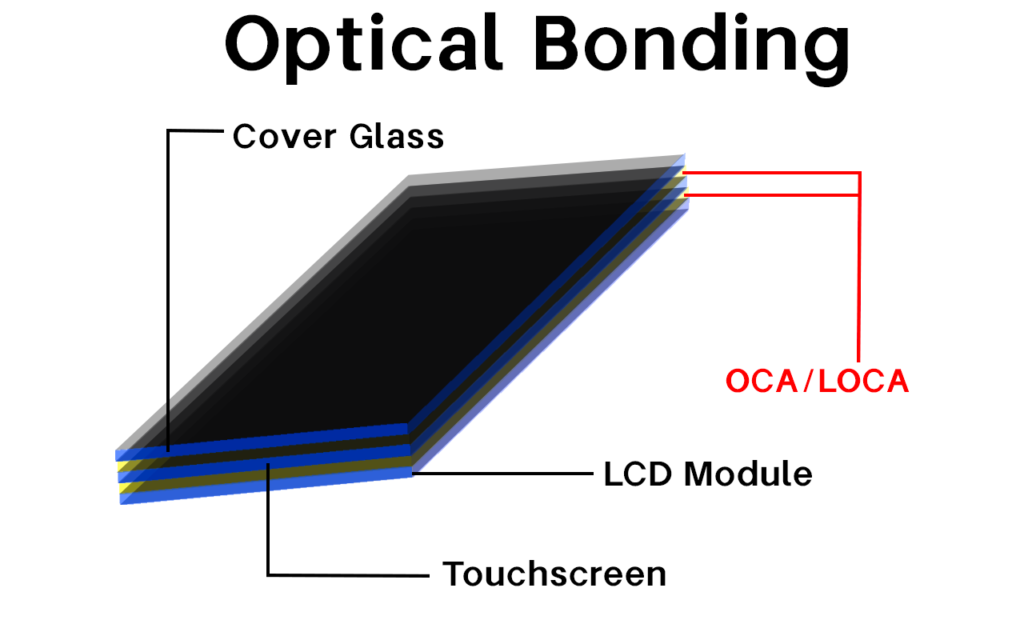
- Uses liquid adhesive (e.g., OCA, epoxy) to permanently bond touchscreens/lens to LCD cells
- Eliminates air gaps for 100% light transmission
- Ideal for indoor/outdoor displays that require durability
Air bonding:
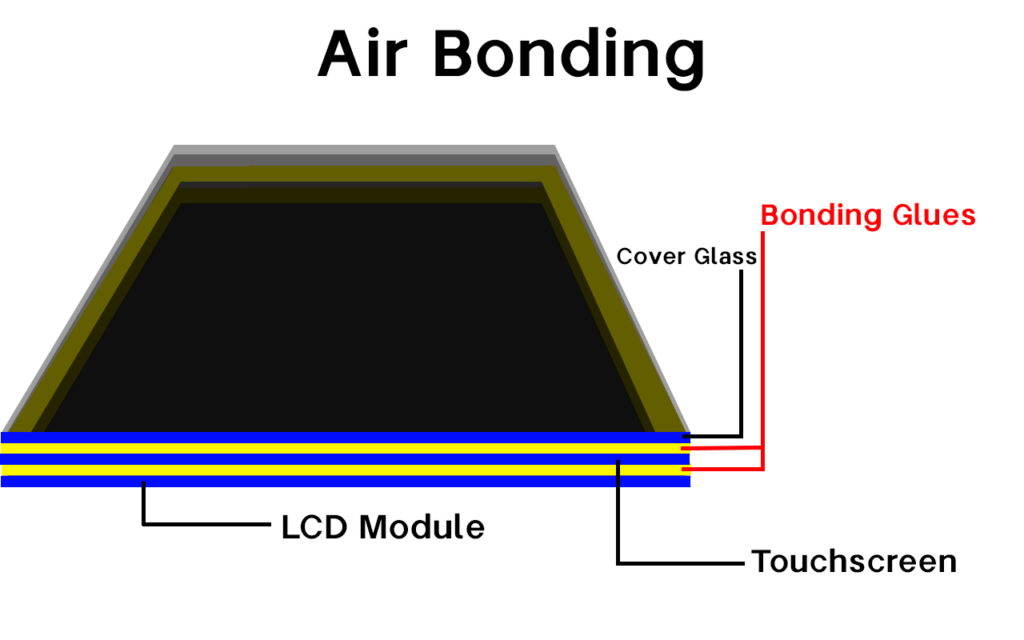
- Relies on mechanical alignment and gravity
- No adhesive used – layers press together via clips/friction
- Suitable for consumer electronics where weight reduction matters
Comparison Table
| Parameter | Optical Bonding | Air Bonding |
|---|---|---|
| Light Transmission | 100% (no air gaps) | 98-99.8% (microscopic gaps) |
| Durability | Higher (scratch/waterproof) | Moderate |
| Cost | 20-30% higher | Cheaper |
| Assembly Time | 3X longer | Faster |
Optical Bonding Process
Optical bonding involves three main techniques: OCA (Optically Clear Adhesive), OCR (Optically Clear Resin), and SCA (Self-Clear Adhesive). Each method serves different applications and requirements.
OCA Bonding uses pre-formed transparent adhesive sheets. The process begins with surface preparation in clean room conditions. The OCA material is carefully positioned and laminated between the touch panel and LCD using specialized equipment. The adhesive can be activated through heat, pressure, or UV light depending on the specific formulation.
OCR/LOCA Bonding employs liquid optical clear adhesive that flows to fill gaps completely. This method requires dispensing the liquid adhesive onto the display surface, positioning the touch panel, and curing the adhesive using UV light. The liquid nature allows for better gap filling but requires more precise process control.
SCA Bonding combines advantages of both methods. The material flows under controlled conditions to eliminate bubbles, then cures to create a strong bond. This method offers excellent reworkability and is particularly effective for larger displays.
How Do Performance Metrics Compare Between Both Technologies?
Which bonding method delivers better results? Performance varies dramatically across metrics.
Optical bonding delivers superior light transmission (>90% vs ~75%), reduced reflection (0.2% vs 13.5%), and enhanced contrast ratios, while air bonding offers higher production yields (99% vs 90%) and lower manufacturing costs(What’s the Real Difference Between Anti-Glare and Anti-Reflective Coatings?).
| Attribute | Optical Bonding Advantages | Air Bonding Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Brightness | Higher (no light scattering) | 0.1-2% reflection loss |
| Touch Sensitivity | Better response (less interference) | Susceptible to alignment shifts |
| Weatherproofing | IP67+ compatibility | Not suitable for wet/moisture |
| Heat Resistance | Stable up to 60°C | Risk of thermal expansion gaps |
Optical Bonding In Action
Outdoor Navigation Displays(What Makes an LCD Sunlight Readable?):
- Challenge: Direct sunlight caused glare
- Solution: Optically bonded glass reduced reflections by 70%
- Result: Easier readability in bright environments
Air Bonding Limitations
While cost-effective, air bonding struggles in:
- Vibration-prone environments (e.g., industrial equipment)
- Extreme temperatures causing CTE mismatches
Which Applications Benefit Most from Each Technology?
| Application | Recommended Bonding | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive dashboards | Optical | Survives temperature/humidity |
| Smartphones | Air (OCA alternative) | Weight/Cost sensitive |
| Public kiosks | Optical | Vandal/dust resistance |
| Wearables (smartwatches) | Air | Thin/light designs needed |
Medical Equipment
Optical bonding dominates here due to(What Special Requirements Do Medical LCD Panels Have?):
- Sterility: No adhesive residue (important in surgical devices)
- Durability: Withstands frequent disinfection cycles
Cost-Critical Designs
Air bonding thrives in:
- Basic e-readers where weight budgets are tight()
- Disposable IoT sensors with 1-year lifespans
What Manufacturing Considerations Impact Your Choice?
Air bonding offers simpler manufacturing with higher yields and lower equipment costs, while optical bonding requires clean room facilities, specialized equipment, and skilled operators but delivers superior product quality.
Optical bonding may reduce yield rates by 5-15% due to alignment challenges, but offers long-term reliability.
| Factory Equipment | Optical Bonding | Air Bonding |
|---|---|---|
| Alignment Machines | Laser positioning systems | Manual/semi-automatic tools |
| Curing Ovens | Required | Not needed |
| Quality Control | Automated optical inspection | Basic visual checks |
| Adhesive Management | Storage under controlled conditions | N/A |
Production Environment Requirements

Air bonding can be performed in standard manufacturing environments with basic equipment. The process requires minimal specialized infrastructure:
- Standard assembly equipment
- Basic adhesive application tools
- Normal environmental controls
- Skilled but not highly specialized operators
Optical bonding demands significantly more sophisticated manufacturing infrastructure:
- Clean room facilities (ISO 9001 or better)
- Specialized bonding equipment for adhesive application
- UV curing systems for light-activated adhesives
- Environmental controls for temperature and humidity
- Highly trained operators with specialized skills
Common Failures
| Bonding Method | Failure Mode | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Optical | Adhesive squeeze-out | Precision die-cutting films |
| Non-uniform curing | Temperature sensors | |
| Air | Alignment drift | Pre-loaded spring clamps |
| Moisture ingress | Hydrophobic sealants |
How Do You Choose the Right Adhesive Types and Selection?
Adhesive quality determines optical bonding success. Let’s decode material options.
Silicone-based adhesives provide excellent thermal stability and reworkability, acrylic adhesives offer superior optical clarity and UV resistance, while polyurethane adhesives deliver exceptional mechanical strength but may yellow over time(What Temperature Range Can LCD Modules Safely Operate In?).
| Adhesive Type | Viscosity (Pa·s) | Curing Time | Tg (°C) | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optically Clear Adhesive (OCA) | 400-800 | 1 hour | -20°C | Touchscreens |
| Silicon-based | 200-600 | 30 mins | -30°C | Flexible displays |
| Epoxy | 100-300 | 4-6 hours | 60°C | Ruggedized modules |
How Does Long-Term Reliability Compare?
Which bonding method holds up better over time? Environmental stress accelerates degradation.
Optical bonding demonstrates superior long-term reliability with 20% better impact resistance and enhanced environmental protection, while air bonding systems show degradation over time due to contamination ingress and seal failure.
| Test Condition | Optical Bonding Survival Rate | Air Bonding Survival Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 hours damp heat | 95% | 60% |
| 1000 thermal cycles | 90% | 40% |
| Vibration resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
Optical Bonding Reliability Advantages
Optical bonding systems demonstrate superior long-term performance:
Moisture Protection: The complete seal provided by optical bonding prevents moisture ingress, eliminating condensation and corrosion risks. This protection is particularly important for outdoor and industrial applications.
Structural Integrity: The bonded assembly provides enhanced structural strength, improving resistance to shock and vibration. This results in longer service life in demanding applications.
Stable Optical Properties: Optical bonding maintains consistent performance over time, with minimal changes in light transmission or reflection characteristics.
Reliability in Specific Environments
Different environments present unique challenges for long-term reliability:
Outdoor Applications: Optical bonding provides superior UV resistance and weather protection, maintaining performance over years of exposure.
Industrial Environments: The contamination resistance of optical bonding systems proves valuable in dusty or chemical environments where air bonding systems would quickly degrade.
Transportation Applications: Vibration and shock resistance advantages of optical bonding translate to improved reliability in mobile applications.
Medical Environments: The contamination resistance and easy cleaning capabilities of optical bonding systems support stringent hygiene requirements while maintaining long-term reliability.
Conclusion
Optical bonding excels in demanding applications requiring reliability and performance, while air bonding suits cost-sensitive consumer electronics. Match methods to specific use cases for optimal results.
FAQ
Will optical bonding affect the repairability or future servicing of LCD modules?
Yes, once glued, separating the glass from the LCD without damage is much harder compared to air-bonded units.
Are there visual differences between optical and air bonding when viewed from different angles?
Optical bonding keeps image quality consistent even at extreme angles, while air bonding may cause internal reflections or ghosting.
Does bonding choice impact warranty terms or after-sales support?
Some suppliers offer longer warranties on optical bonded modules because they are more robust and less likely to fail outdoors.
What causes air bubbles in optical bonding and how can they be prevented?
Air bubbles form during improper mixing or application of adhesives, and can be prevented by using proper mixing techniques, vacuum degassing, and controlled application environments
How long does optical bonding last compared to air bonding?
Optical bonding typically lasts 5-10 years even in harsh conditions while air bonding lasts 3-7 years, but optical bonding’s lifespan depends heavily on proper installation and adhesive quality