Choosing a display screen can be confusing. Making the wrong choice can lead to a frustrating user experience and wasted money. Let’s break down these technologies to find your perfect fit.
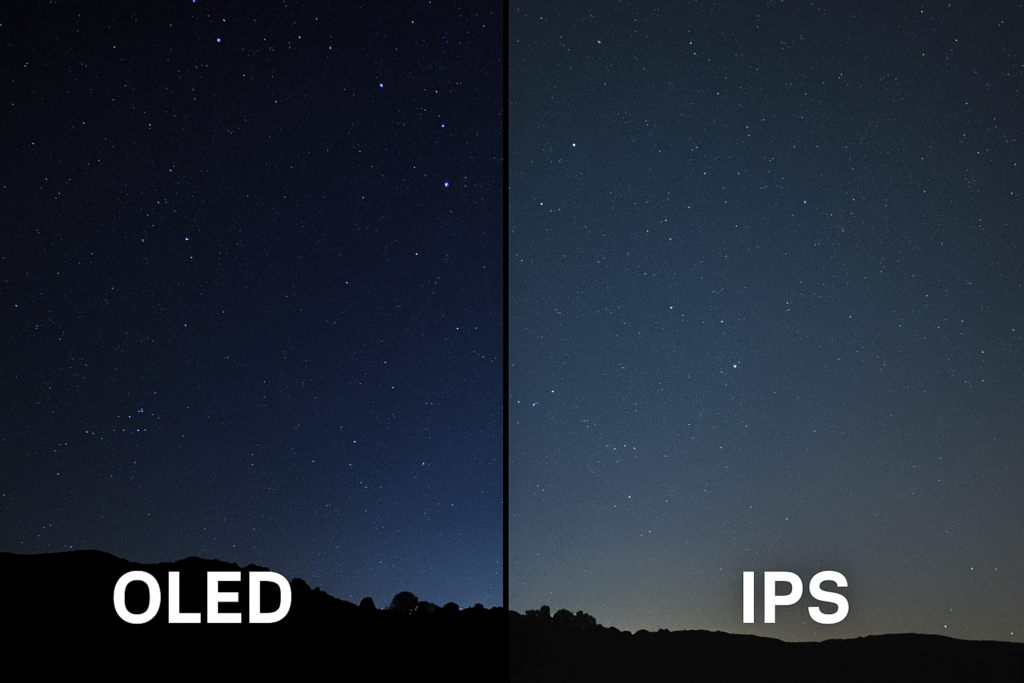
OLED displays offer superior contrast and vibrant colors but are more expensive and risk burn-in. IPS displays provide excellent color accuracy and wide viewing angles at a lower cost, making them more durable for general use.
I once had a client, who was stuck on this exact problem. He was developing a new smartwatch and the screen choice was critical. His decision would define his product’s quality and reliability.
What Are the Core Differences Between IPS and OLED Displays?
The fundamental difference between ips vs oled isn’t just marketing. It’s about how each screen physically creates light and color, which impacts everything you see.
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) pixels create their own light, allowing for true blacks and what we call an infinite contrast ratio. An IPS (In-Plane Switching) display, a type of LCD, uses a single backlight to illuminate all its pixels.
How They Work
1. How Light Is Produced
An amoled panel (Active-Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) is made of millions of tiny light bulbs. Each pixel can be turned on or off independently. When a pixel is off, it emits no light, creating a perfect, true black. This self-emissive nature is the key advantage of oled displays over ips displays. It allows for incredibly thin and flexible screens because it doesn’t need a separate backlight layer.
On the other hand, an ips panel is a type of led backlit lcd display. Think of it as a very sophisticated light filter. There is a powerful LED backlight that is always on when the display is active. The In-Plane Switching liquid crystals then twist or align to block that light or let it pass through color filters to create the image on the screen. Because the backlight is always there, it’s impossible to achieve a perfect black; some light always bleeds through, which is why blacks on an ips lcd vs led (OLED) can sometimes look slightly gray(Why Do IPS LCD Screens Contain Polarizing Filters Inside?).
2. Impact on Image Quality
This core difference in how light is produced directly affects what you see.
- Contrast: OLED wins, hands down. The ability to turn pixels completely off results in an “infinite” contrast ratio. This makes images look incredibly punchy and realistic, especially in dark scenes in movies or games. An ips tft lcd has a fixed contrast ratio, typically around 1000:1, which is good but cannot compete with the depth of an OLED.
- Color: OLEDs are known for their vibrant, saturated colors that seem to “pop” off the screen. They can display an extremely wide range of colors. IPS screens are famous for their color accuracy. For years, professionals have relied on the panel ips vs led (or other LCD types) for photo and video editing because they reproduce colors faithfully and consistently(How Do Manufacturers Ensure Color Accuracy in Production?).
- Viewing Angles: Both technologies offer excellent viewing angles. You can look at either an IPS or an OLED screen from the side with minimal color shift. This was a huge improvement that IPS technology brought over older TN panels and a strength that OLED technology shares.
What Are the Pros and Cons of IPS and OLED Displays?
Every display technology involves trade-offs. The oled vs ips display choice is a classic example of balancing cutting-edge performance against proven reliability and cost-effectiveness.
OLED’s advantages are its stunning visual quality and fast response time, but its disadvantages include burn-in risk and high cost. IPS’s pros are durability, affordability, and great color accuracy, with its main con being a lower contrast ratio.
A Head-to-Head Comparison
| Feature | OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) | IPS (In-Plane Switching) |
|---|---|---|
| Contrast Ratio | Infinite (True, perfect blacks) | Good (Typically 1000:1, blacks can look grayish) |
| Color Performance | Extremely vibrant, wide color gamut, high saturation | Excellent color accuracy and consistency |
| Response Time | Extremely fast (often under 0.1ms), no motion blur | Good (1-5ms), but generally slower than OLED |
| Viewing Angles | Excellent, with no color or contrast shift | Excellent, with minimal color shift |
| Burn-in Risk | A real risk with static images over time | None |
| Lifespan | Generally shorter as organic materials degrade | Very long and durable |
| Cost | High (Premium) | Affordable to Moderate |
| Brightness | Good, but can be limited compared to the brightest IPS | Can achieve very high peak brightness levels |
How Do IPS and OLED Compare in Different Use Cases?
The “better” display truly depends on what you are doing. A gamer’s priorities are different from a graphic designer’s, and different again from someone doing office work.
OLED excels in media consumption and gaming thanks to its perfect blacks and instant response times. IPS is the reliable workhorse for professional creative work and general productivity due to its color accuracy, longevity, and lower cost.
The Right Tool for the Job
1. For Gamers
The oled vs ips battle is fierce in the gaming world. OLEDs offer an incredibly immersive experience. The per-pixel lighting makes HDR content look breathtaking, and the near-instantaneous response time means there is zero ghosting or motion blur in fast-paced games. The main drawback is the risk of burn-in from static game elements like health bars or mini-maps left on screen for hundreds of hours.
An ips screen vs led (OLED) is the safer bet for many gamers. Modern IPS gaming monitors offer high refresh rates and very low response times that are more than enough for competitive gaming. You get great colors and wide viewing angles without any anxiety about screen burn-in.
2. For Content Creators (Photo & Video Editing)
Traditionally, IPS has been the undisputed king for any color-critical work. Professionals trust ips panel displays for their dependable color accuracy. When you edit a photo on an IPS screen, you can be confident that the colors will look the same when printed or viewed on other high-quality screens.
OLEDs are starting to challenge this. High-end amoled panel displays can now be calibrated for professional-grade accuracy. Video editors, in particular, love OLEDs because the true blacks allow them to see every detail in shadowy footage. However, the potential for burn-in and the higher cost are still significant considerations.
3. For General Use (Office Work, Browse)
For everyday tasks, an ips panel vs led (OLED) is a clear choice for most people. IPS technology is more than good enough for viewing text, Browse websites, and working on documents. More importantly, it is affordable and completely immune to burn-in from static interface elements like a taskbar or application windows that are on-screen all day. Using an OLED for this type of work introduces unnecessary risk and cost.
How Do You Decide Which Display Is Right for You?
Now that you understand the technology and the trade-offs, making the right choice is much simpler. It comes down to your personal priorities and how you plan to use the screen.
Choose OLED if your top priority is the absolute best image quality for an immersive movie or gaming experience and you can afford the premium. Choose IPS for a versatile, color-accurate, and durable display for any combination of work, gaming, and general use.
A Practical Checklist
Let’s go back to my clien. To help him, I had him answer a few simple questions:
- What is your primary use case? For his smartwatch, the screen would frequently close screen or open screen to show data like speed, distance, and battery level.
- What is your environment? The device would be used outdoors in bright sunlight.
- What are your biggest concerns? For a commercial product, reliability, longevity, and cost are paramount.
For my client, the choice was clear. An ips tft lcd was the perfect solution. It could get very bright for outdoor visibility, had no risk of burn-in from the static interface, and was far more cost-effective for mass production.
Related Articles:
What Is a Frame Buffer and How Does It Work in Embedded Systems?
How can I reduce LCD power consumption in embedded systems?
How do timing controllers (TCON) synchronize image data in LCDs?
What Is the Typical MTBF for Commercial LCD Modules?
Should You Use Custom Display Layers or HALs for LCD Integration?
Conclusion
Both OLED and IPS are fantastic technologies. Your final choice simply depends on balancing your desire for visual perfection against your need for practicality, longevity, and affordability.
FAQ
Is OLED worth the extra money in 2025?
If you are a cinephile or competitive gamer who prioritizes perfect blacks and instant response times, the premium for OLED can be worth it. For most other users, a high-quality IPS display offers better overall value and durability.
Which display technology lasts longer?
IPS panels generally have a longer functional lifespan as they are a more mature technology not prone to burn-in. OLED screens can degrade over time, particularly the blue organic material, which can lead to color shifting after many thousands of hours.
Does OLED or IPS use more battery power on a laptop?
OLED displays are more power-efficient when showing dark content since their pixels are off, but IPS can be more efficient when displaying bright, white-heavy content like documents. Overall battery impact depends heavily on your usage patterns.
Are all LED displays the same as IPS displays?
No. IPS is a type of LCD panel; LED refers to the backlight. Not all LED displays use IPS panels – they may use TN or VA technologies.
Is color accuracy better on IPS or OLED?
IPS panels traditionally offer better color accuracy, especially in calibrated professional monitors. OLED has improved but can vary across models.