TN, IPS, and VA panels interact differently with backlighting, influencing display brightness, color accuracy, and energy efficiency. The design of a backlighting system must be tailored to the characteristics of each panel type to ensure optimal performance(Difference between IPS TFT and TN TFT).
TN panels require high brightness due to their narrow viewing angles and lower color accuracy. Edge-lit or direct-lit LED backlighting is commonly used to enhance visibility while keeping costs low.
IPS panels demand uniform, diffused backlighting to maintain color accuracy and reduce distortion. These panels often integrate Quantum Dot technology or mini-LED solutions to expand the color gamut and improve brightness control.
VA panels benefit from advanced dimming technologies to manage contrast and minimize backlight bleed. Full-array local dimming is often used to maintain deep blacks while preventing unwanted light leakage.
Energy efficiency also varies across panel types, impacting display design. IPS panels consume more power due to precise light control, while TN panels rely on high brightness to compensate for visual limitations. Manufacturers use adaptive brightness and local dimming to optimize power consumption without sacrificing display performance(What is HDR Technology: Local Dimming, Global Dimming).
The choice of backlighting technology directly influences production costs. High-end solutions like mini-LEDs and OLED-based systems enhance performance but increase manufacturing expenses. Balancing cost and efficiency is key when designing backlighting systems for different LCD panel technologies.
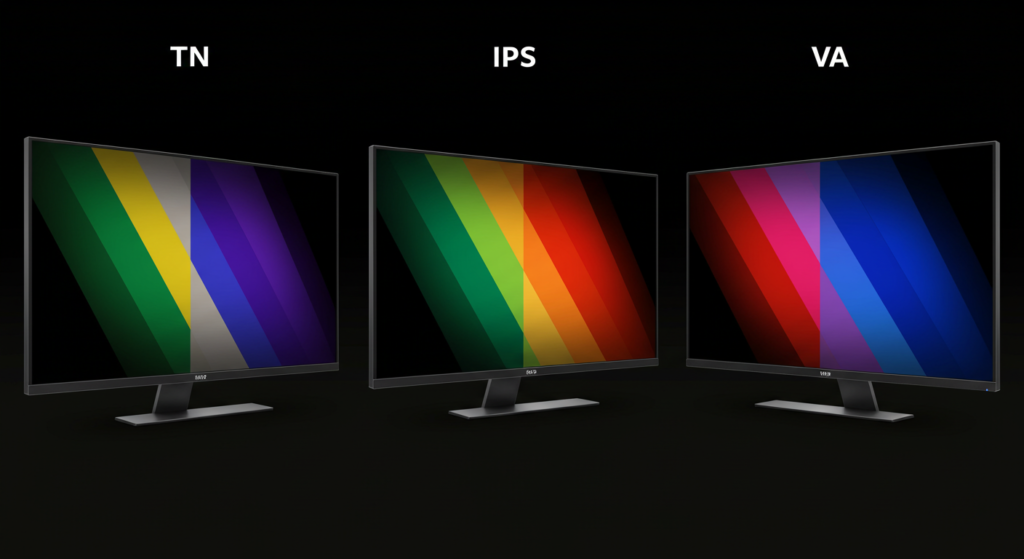

What is Panel Technology? What are the Characteristics of Different Panel Types?
Panel technology refers to the type of panel used in displays to generate images. Common panel technologies include TN, IPS, and VA, each with distinct performance characteristics and backlighting requirements.
In LCD technology, the panel type directly affects display quality and cost. TN panels are widely used in gaming monitors due to their fast response time and low cost, but they have poor color accuracy and narrow viewing angles. IPS panels are known for their high color accuracy and wide viewing angles, though they tend to be slower and more expensive. VA panels offer excellent contrast ratios and deep blacks but suffer from backlight bleed. They are ideal for watching movies and high-contrast content, though they are more prone to light leakage.
- TN Panels: TN panels, due to their fast response time and low cost, typically employ basic LED backlighting solutions. They are suitable for users with budget constraints and who do not require precise color accuracy. Since they have narrow viewing angles, they often need higher brightness levels to maintain visibility from various angles.
- IPS Panels: IPS panels require more uniform backlighting, often using more advanced LED backlight technology to ensure consistent color accuracy. IPS panels have higher brightness requirements and a greater need for diffusion and uniformity in backlighting to avoid color shifts and inconsistencies.
- VA Panels: VA panels are recognized for their superior contrast ratios, with deep black levels. To prevent backlight bleed, VA panels often incorporate advanced local dimming technology or edge-lit backlighting solutions, ensuring the display maintains high contrast levels without light leaks.
How Does Panel Technology Affect Backlighting Design?
Panel technology significantly influences backlighting design. Different panel types have unique backlighting needs, which impact brightness, uniformity, and color performance.
Each panel technology has specific requirements for backlighting. TN panels, while less concerned with color accuracy, require higher brightness levels to compensate for their narrow viewing angles. IPS panels, on the other hand, need more uniform backlighting to ensure color stability, reducing the chance of color shifting. VA panels, which excel at contrast ratios, focus on minimizing light leakage, often using precise local dimming or edge-lit backlighting methods.
TN Panels usually utilize high-brightness LED backlighting to compensate for their limited color accuracy and narrow viewing angles(Illuminate Your Space: Uniform Backlight Side LEDs?).
How Does Panel Type Affect Backlighting System Design?
The type of panel affects how light is distributed, absorbed, and reflected, which directly influences the efficiency and uniformity of the backlighting system.
The properties of each panel type—such as light scattering, absorption, and reflection—play a key role in the design of backlighting systems. TN panels, due to their lower color accuracy, require bright and direct light sources to ensure visibility, often compromising on color consistency. IPS panels demand diffused light sources to maintain uniformity and minimize color distortion, ensuring an even distribution of light. VA panels, with their strong contrast ratios, require advanced backlight control systems (such as full-array backlighting) to avoid light leakage and preserve deep black levels.
- TN Panels: Due to their poor color accuracy and narrow viewing angles, TN panels typically require higher brightness and more direct LED light sources. This helps compensate for the lack of color consistency, but can result in a less uniform backlight.
- IPS Panels: IPS panels are designed for superior color accuracy and wider viewing angles. To maintain uniform light distribution and prevent color shifts, they require diffused backlighting solutions that spread light evenly across the display. This ensures that colors appear consistent, even from different angles.
- VA Panels: VA panels excel in delivering deep blacks and high contrast ratios. To maintain this high contrast without compromising visibility, they often use advanced backlight control techniques like full-array backlighting or local dimming. These solutions reduce backlight bleed and prevent light leakage, ensuring that the blacks remain deep and the overall display quality is sharp.
What Are the Specific Backlighting Needs for Different Panel Types?
Different panel types have specific backlighting needs based on their light distribution, absorption, and reflection properties.
TN panels need bright, direct light sources due to their limited color accuracy and narrow viewing angles. IPS panels require more uniform, diffused backlighting to preserve color accuracy and consistency across wider viewing angles. VA panels, with their high contrast and deep blacks, need advanced backlight systems like full-array or local dimming to prevent light leakage and maintain high-quality visual contrast.
TN panels often use brighter, more direct LED light to overcome their color accuracy limitations, but this can affect backlight uniformity.
How Does Backlighting Affect Color Reproduction in Different Panel Types?
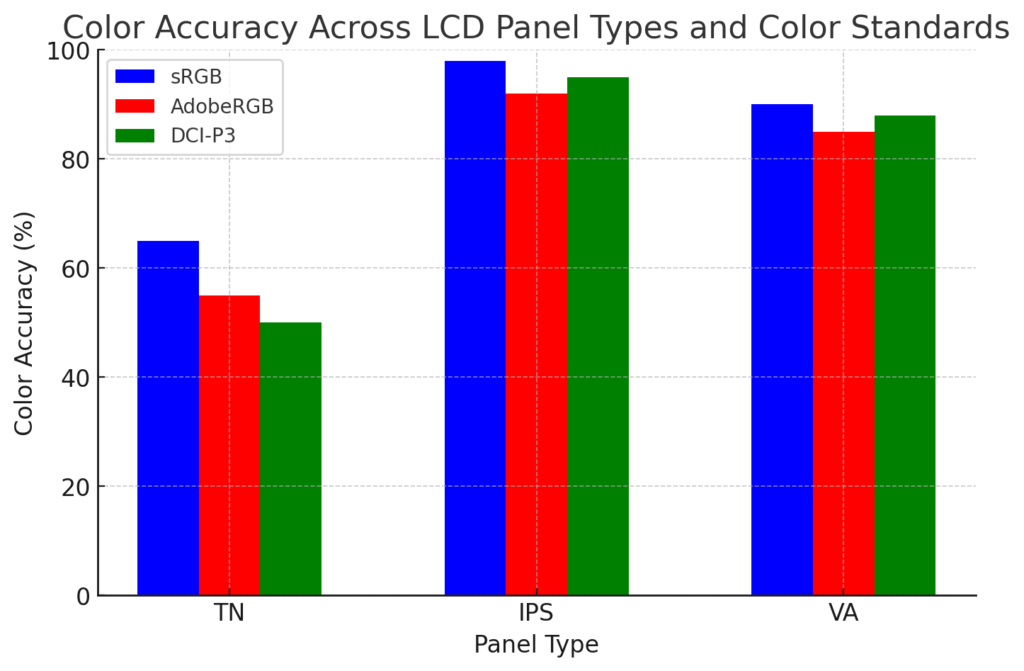
Backlighting plays a crucial role in color accuracy, with different panel types reacting differently to light distribution. IPS panels, in particular, require more advanced backlighting systems to maintain color consistency.
Each panel type interacts differently with backlighting, influencing how accurately colors are displayed. TN panels, which prioritize speed over color accuracy, use simpler backlighting systems. IPS panels, known for their precise color reproduction, require more sophisticated backlighting technologies, such as Quantum Dots or OLED-based solutions, to ensure uniform color accuracy. VA panels, with their high contrast ratios, need carefully designed backlighting to prevent color shifts and uneven illumination.
- TN Panels: TN panels are less dependent on advanced backlighting, as they do not prioritize high color accuracy. A basic LED backlight is often sufficient, making them more cost-effective.
- IPS Panels: IPS panels require highly controlled, diffused backlighting to maintain color uniformity across the screen. Technologies like Quantum Dots can enhance color performance by expanding the color gamut without increasing energy consumption.
- VA Panels: The interaction between backlighting and VA panels’ high contrast ratios can create uneven color distribution. To minimize this, edge-lit or full-array local dimming techniques are often used to control light precisely and prevent unwanted color shifts.
What Backlighting Technologies Improve Color Accuracy?
Advanced backlighting technologies, such as Quantum Dots and local dimming, help improve color accuracy, particularly in IPS and VA panels.
Quantum Dot technology enhances color saturation and accuracy by improving the quality of emitted light. Local dimming optimizes contrast and brightness distribution, ensuring accurate color rendering in VA and IPS displays.
- Quantum Dot backlighting expands the color gamut in IPS panels, making colors appear more vibrant without increasing power consumption.
- Local dimming and edge-lit designs improve color uniformity by reducing light leakage, particularly in VA panels, where contrast control is essential.
What Are the Manufacturing and Design Challenges in Backlighting Systems?
Manufacturing backlighting systems for different panel types presents challenges in uniformity, backlight bleed, and cost efficiency. Designers must balance performance and cost while ensuring optimal light distribution.
Backlighting systems must be carefully designed to prevent issues like uneven illumination and backlight bleed, which are especially problematic in VA panels due to their high contrast nature. IPS panels require precise light diffusion to maintain color accuracy, making their backlighting solutions more complex and costly. TN panels, though simpler, still require adequate brightness control. Manufacturers must choose between edge-lit, full-array, or local dimming solutions to optimize uniformity while controlling production costs.
- Uniformity and Backlight Bleed Solutions:
- VA panels often suffer from backlight bleed due to their strong contrast, requiring full-array backlighting or local dimming to distribute light evenly.
- IPS panels rely on uniform light diffusion, making high-quality LED backlighting a necessity to avoid color inconsistencies.
- TN panels use simpler backlight solutions, though achieving consistent brightness across the screen remains a challenge.
- Cost Considerations in Backlighting Design:
- IPS displays need advanced, expensive backlighting systems to maintain accuracy, increasing production costs.
- VA panels require more precise dimming control, adding to manufacturing complexity.
- TN panels, being more budget-friendly, use basic LED backlights but may trade off uniformity and quality.
How Can Manufacturers Balance Cost and Performance in Backlighting Systems?
The key to balancing cost and performance lies in selecting the right backlighting technology based on the panel type and intended use.
Manufacturers optimize costs by choosing between edge-lit and full-array backlighting. Edge-lit designs are more affordable but may have uneven brightness, while full-array backlighting with local dimming improves uniformity but increases costs. Selecting energy-efficient LEDs and adaptive brightness control can further reduce power consumption without compromising display quality.
- Edge-lit backlighting reduces production costs but may cause uneven illumination, especially in VA and IPS panels.
- Full-array local dimming enhances uniformity and contrast but increases manufacturing expenses, making it more common in premium displays.
- Adaptive brightness control helps balance energy efficiency while maintaining consistent display performance.
What Are the Best Backlighting Solutions for Different Panel Types?
Optimizing backlighting for different panel types requires custom solutions. TN, IPS, and VA panels benefit from different technologies like edge-lit, direct-lit, or full-array backlighting to enhance performance and efficiency.
Each panel type requires a specific backlighting approach to maximize its strengths and minimize weaknesses. TN panels, due to their lower color accuracy, can use edge-lit or direct-lit solutions for cost efficiency. IPS panels need diffused lighting to maintain uniform color consistency. VA panels, which excel in contrast, benefit from full-array local dimming to prevent backlight bleed. Manufacturers also incorporate advanced LED technologies such as Quantum Dots, mini-LEDs, and OLED to solve challenges related to energy efficiency and color accuracy.
- Custom Backlighting for Different Panel Types:
- TN panels: Best suited for edge-lit or direct-lit LED backlighting due to their lower demand for color precision.
- IPS panels: Require diffused LED backlighting to ensure even brightness and prevent color shifts.
- VA panels: Benefit from full-array local dimming to manage contrast and reduce backlight bleed.
- Advanced LED Technologies for Better Performance:
- Quantum Dot backlighting expands color gamut, improving color accuracy in IPS and VA panels.
- Mini-LEDs and OLED enable higher brightness control, reducing backlight bleed and power consumption.
- Local dimming solutions improve contrast, making VA panels ideal for high dynamic range (HDR) content.
How Can Backlighting Improve Energy Efficiency?
Smart backlighting solutions, such as adaptive brightness and local dimming, help reduce power consumption while maintaining display quality.
By incorporating adaptive brightness control, displays can adjust backlight intensity based on content and ambient light levels, improving energy efficiency. Local dimming selectively reduces brightness in darker areas, optimizing power usage in IPS and VA displays.
- Adaptive brightness sensors adjust backlighting levels dynamically, reducing power usage in well-lit environments.
- Local dimming and energy-efficient LEDs cut down on unnecessary power consumption while maintaining image quality.
- Mini-LED and OLED technology provide better brightness control, making high-end displays more energy-efficient.
Conclusion
The design of backlighting systems is directly influenced by the type of LCD panel used. TN panels require high brightness due to their narrow viewing angles, IPS panels need uniform diffused lighting for accurate color reproduction, and VA panels benefit from full-array local dimming to maintain contrast. Manufacturers optimize performance and energy efficiency by using technologies like Quantum Dots, mini-LEDs, and adaptive brightness control, balancing cost and display quality for different use cases.
FAQ
What is the best backlighting type for IPS panels?
IPS panels require uniform and diffused backlighting to maintain color accuracy and viewing angles. Edge-lit or full-array LED backlighting with local dimming is ideal for optimal performance.
Why do IPS panels consume more power than TN or VA panels?
IPS panels require a more precise light control system to ensure accurate color reproduction, which leads to higher power consumption compared to TN and VA panels.
How does backlight bleed affect VA panels?
VA panels offer high contrast ratios, but they are prone to backlight bleed, which can cause uneven brightness and affect dark scene performance. Using well-designed local dimming or direct-lit backlighting can help reduce this issue.
What is the most energy-efficient backlighting for LCD monitors?
LED backlighting with adaptive brightness or local dimming helps reduce energy consumption while maintaining brightness levels and display quality.
How do LED backlights impact color accuracy in LCD displays?
LED backlighting with adaptive brightness or local dimming helps reduce energy consumption while maintaining brightness levels and display quality.
Are there cost-effective solutions for improving TN panel backlighting?
Yes, edge-lit LED backlighting provides a cost-effective solution for TN panels by offering adequate brightness while keeping production costs low.
Can IPS panels suffer from backlight bleed?
Yes, IPS panels can experience backlight bleed, but using a high-quality diffuser and proper panel assembly can help minimize this effect.
What’s the difference between an LED-backlit LCD and an OLED display?
LED-backlit LCDs use a backlight to illuminate the pixels, while OLED displays generate their own light per pixel, leading to better contrast and true blacks.
How can I reduce flickering in my LED backlight monitor?
LED-backlit LCDs use a backlight to illuminate the pixels, while OLED displays generate their own light per pixel, leading to better contrast and true blacks.
Is local dimming necessary for gaming monitors?
Is local dimming necessary for gaming monitors?