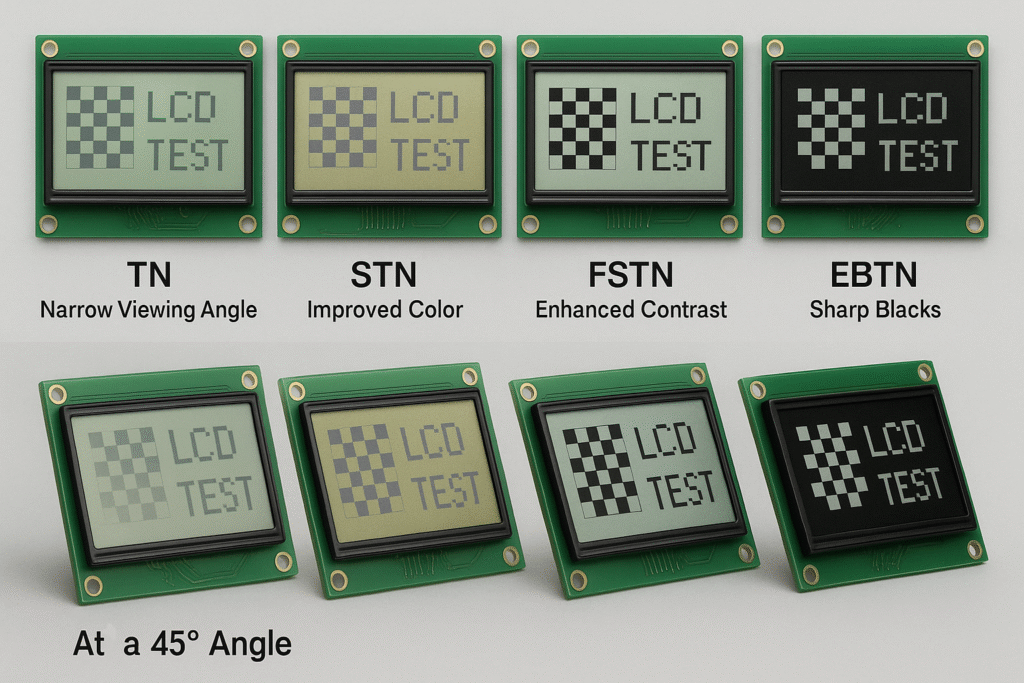
Choosing the right LCD module can be confusing. There are many types—TN, STN, HTN, FSTN, DFSTN, EBTN. Picking the wrong one causes poor results and wasted time.
TN, STN, HTN, FSTN, DFSTN, and EBTN LCDs all use twisted nematic crystals, but each type has a different structure and performance. Viewing angle, contrast, and price all change based on type.
Years ago, I struggled with LCD selection on a new project. Understanding twist angles and construction made all the difference for product performance.
Liquid-Crystal Fundamentals: Why Twist Angle Matters?
The heart of LCDs is the way liquid crystals twist. The twist angle affects how light passes through the screen and impacts the display’s qualities(How does viewing angle relate to LCD backlight design?).
Twist angle means how much the liquid crystals turn the light inside the display. The angle changes the viewing angle, contrast, and speed.
How Does Twist Angle Affect Performance?
| LCD Type | Twist Angle | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| TN | 90° | Fast, low cost |
| HTN | 110–130° | Improved angle |
| STN | 180–270° | Wider angle, better color |
| FSTN | 180–270° | Film for sharp contrast |
| DFSTN | Dual | Highest contrast |
| EBTN | Variable | Sharp blacks, top view |
Why Use Different Angles?
Small twists make for quick displays, but bad side views. High twists give stable colors and wide angles, but cost more and can be slower.
Side-by-Side Technical Matrix?
It’s hard to compare LCD types without a clear table. Many people ask, “Which is best?” But each type has pros and cons.
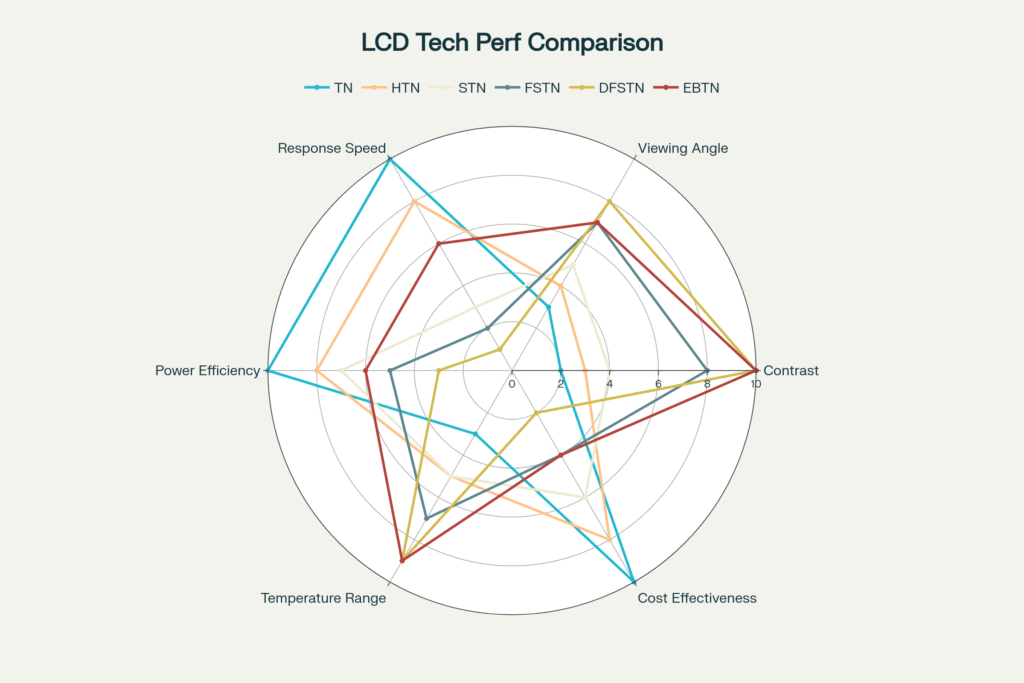
Each LCD type offers a unique balance of speed, viewing angle, contrast, power use, and price. The right one depends on your project’s needs(How Do Dual-Layer LCDs Enhance Contrast Ratios?).
Technical Comparison Table
| Feature | TN | HTN | STN | FSTN | DFSTN | EBTN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Twist Angle | 90° | 110–130° | 180–270° | 180–270° | 180–270° | Variable |
| Viewing Angle | Narrow | Medium | Wide | Wider | Widest | Best |
| Contrast | Low | Medium | High | Higher | Highest | Sharpest |
| Response Time | Fast | Fast | Medium | Medium | Slow | Fast |
| Power Use | Low | Low | Medium | Medium | High | Medium |
| Cost | Lowest | Low | Medium | Med-High | High | High |
Key Technical Points
- TN is cheap and fast, but not good for side viewing.
- STN is good for portable, clear devices.
- FSTN adds a film for better black and white.
- DFSTN is the best for high-contrast but costs more.
- EBTN gives strong blacks and top performance.
Performance Under Environmental Extremes?
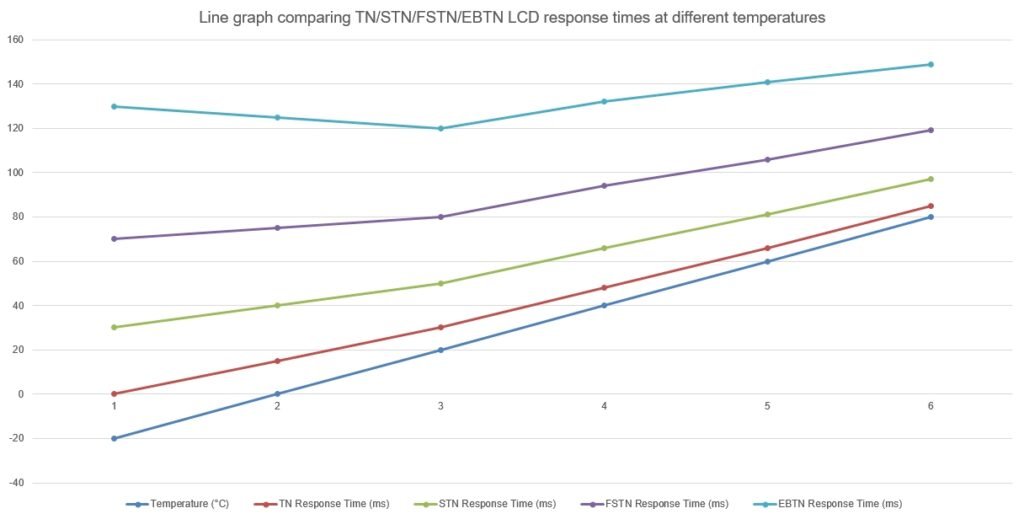
Many projects need LCDs to work in tough places. Heat, cold, water, and shock test every display’s limits(What Temperature Range Can LCD Modules Safely Operate In?).
LCD performance in extreme conditions depends on the display’s structure. TN is less stable, but DFSTN and EBTN handle hard conditions better.
Temperature and Humidity Ranges
| LCD Type | Operating Temp (°C) | Humidity Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| TN | 0–50 | Low |
| HTN | -10–60 | Medium |
| STN | -10–60 | Medium |
| FSTN | -20–70 | Good |
| DFSTN | -30–80 | Very Good |
| EBTN | -30–85 | Excellent |
Real-World Examples
I remember one American customer making e-bike screens. Their TN displays failed in winter. Cold weather turned the screens black. We moved to DFSTN, which worked even in snow. Another customer needed screens for boats in Florida. EBTN modules handled heat and wet air with no fading(How Do LCDs Behave at Sub-Zero Temperatures?).
Application-Driven Selection Guide?
Every display has a best use. Start by asking, “Where will the product live? Who will use it?”
TN is good for simple, low-cost devices. EBTN is best for critical, high-end projects that need top performance.
Application Mapping Table
| Application | LCD Type |
|---|---|
| Calculators, clocks | TN |
| Simple meters | HTN |
| Phones, POS, e-readers | STN, FSTN |
| Car, outdoor displays | FSTN, DFSTN |
| Medical, industrial | EBTN |
Customer Stories
I worked with my client from the US, who builds bike displays. At first, STN showed glare in sunlight. We switched to FSTN, and his product looked much sharper(How Do Sunlight-Readable LCDs Maintain Contrast Outdoors?).
Integration Considerations for Engineers?
A perfect display on paper means nothing if it doesn’t fit the device. Engineers need to check voltage, interface, and size.
You must match LCD electrical and size needs to your product. Check specs before buying or you risk delays and mistakes.
Common Integration Checklist
- Supply voltage
- Pinout and connection type
- Driver IC support
- Display resolution
- Backlight requirements
- Physical size
Typical Integration Issues
I often see engineers order high-end EBTN screens but forget to check if their board supports the right voltage. Some use FSTN but skip the backlight power check, so the screen looks dark at night. Always test samples before mass production(What Is the Right Way to Use Level Shifters With 3.3V LCD Modules in 5V Systems?).
Comparison with Modern Alternatives?
Are traditional LCDs “out of date” against OLED or TFT? It depends on the need.
OLED offer great color and fast video, but classic LCDs are more reliable, cheaper, and easier to read outdoors(Exploring Smartwatch Displays: The Difference Between AMOLED and LCD Displays).
When Is LCD Better?
| Feature | TN/STN LCD | OLED | TFT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Use | Lowest | High | Medium |
| Sunlight Readable | Yes | No | Limited |
| Cost | Low | High | Medium |
| Life Span | Long | Medium | Medium |
| Color | Mono | Full | Full |
I recommend LCD for simple, long-life products or outdoor screens. OLED and TFT are better for color-rich and video products, but they cost more.
Emerging Enhancements?
LCD tech keeps getting better. Even classic designs have new tricks now.
New materials and coatings give EBTN, DFSTN, and hybrids sharper images, longer life, and better sunlight performance.
What’s New in LCDs?
- Anti-reflective films for clearer images
- Polarizers for better sunlight reading
- Faster liquid crystals for quick refresh
- Touch integration for smarter displays
Some new EBTN screens use color backlights, making mono screens nearly as useful as color ones for many jobs.
Conclusion
Every LCD type suits a different need. Choosing the right one means better products and happier users.
FAQ
Can I use TN LCDs for battery-powered devices?
TN LCDs consume low power, making them ideal for battery-powered devices. Ensure narrow viewing angles meet your needs.
How do I ensure LCD reliability in humid environments?
FSTN and DFSTN resist humidity better than TN. Choose them for applications exposed to moisture.
Are these LCDs suitable for high-speed dynamic displays?
TN and EBTN support fast response times for dynamic displays. STN and FSTN are better for static images.
What if I need a non-standard LCD shape?
FSTN, DFSTN, and EBTN support custom shapes. Discuss your requirements with suppliers early.
How do I address color limitations in monochrome LCDs?
Monochrome LCDs like EBTN offer high contrast but no color. Use TFT for color-critical applications.