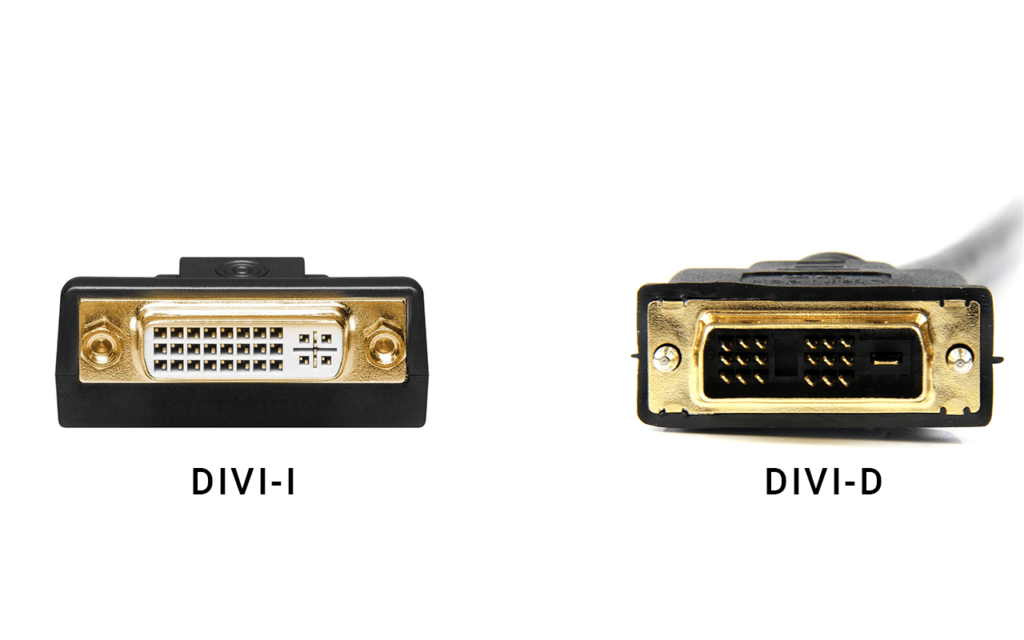
Have you ever tried connecting a monitor and ended up staring at a blank screen or a blurry image? You’re not alone. One of the most common reasons for this problem is misunderstanding the difference between DVI-I and DVI-D connectors.
DVI-I connectors support both digital and analog signals, making them versatile for a wide range of displays. In contrast, DVI-D connectors support only digital signals and are better suited for modern LCD monitors.
Understanding which DVI connector to use can save you time and money. It also helps you avoid compatibility issues when setting up or upgrading your display systems. Many of my clients have run into issues that could have been avoided with just a little background knowledge on DVI.
What's the Core Technical Distinction of DVI-I and DVI-D?
Do you ever wonder what those white ports on the back of your monitor or graphics card are for?
DVI stands for Digital Visual Interface. It’s a video interface designed to transmit high-quality digital video signals from a computer to a display, like a monitor or projector.
Dive Deeper into the World of DVI
DVI was developed to replace the older VGA standard, which only supports analog signals. With DVI, you can transmit digital signals without converting them, preserving image quality. DVI also supports analog signals, making it a bridge between older and newer technology.
Here are the main types of DVI connectors:
| Type | Signal Type | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| DVI-D | Digital | Digital displays, modern LCD monitors |
| DVI-I | Integrated | Works with both digital and analog displays |
| DVI-A | Analog | Older CRT monitors |
What's the Core Technical Distinction of DVI-I and DVI-D?
Why does one DVI cable work while another doesn’t?
DVI-I has extra pins to support analog signals in addition to digital, while DVI-D lacks those analog pins and transmits only digital data.
A Closer Look at Connector Structure
DVI-D (Digital Only):
- Lacks the four analog pins surrounding the flat blade pin.
- Supports digital signal transmission only.
- Ideal for modern displays that only accept digital input.
DVI-I (Integrated Digital and Analog):
- Includes the four extra analog pins.
- Compatible with both analog (VGA) and digital (DVI-D) inputs.
- Can be used with passive DVI to VGA adapters.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | DVI-I | DVI-D |
|---|---|---|
| Supports Analog | Yes | No |
| Supports Digital | Yes | Yes |
| Extra Pins | Yes (4 around blade) | No |
| Adapter Compatibility | VGA/DVI-D | HDMI/DVI-D |
DVI-I cables are backward compatible with DVI-D ports, but not the other way around. Always check the pin layout before plugging in a cable.
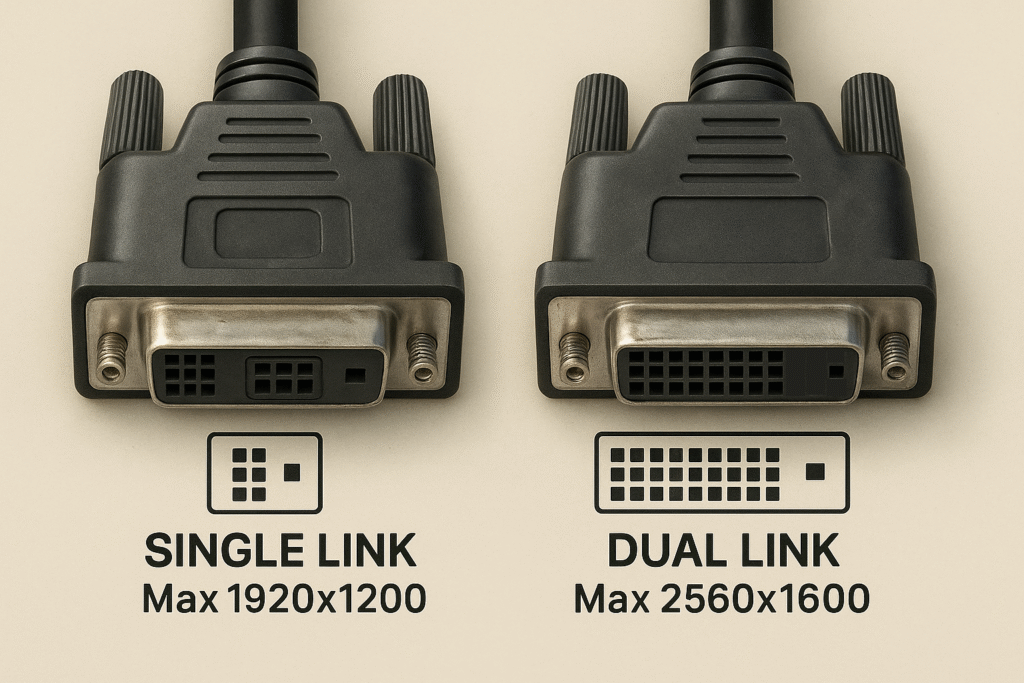
Do Single-Link and Dual-Link Matter for My Display?

Trying to run your monitor at high resolution but the image doesn’t look right?
Yes, single-link cables support up to 1920×1200 resolution, while dual-link cables support up to 2560×1600, making them essential for high-resolution or large monitors.
What’s the Difference Between Them?
Single-Link DVI:
- Uses fewer pins.
- Suitable for standard displays.
- Bandwidth: ~4.95 Gbps.
Dual-Link DVI:
- Has more pins to double bandwidth.
- Required for higher resolutions and refresh rates.
- Bandwidth: ~9.90 Gbps.
| Link Type | Max Resolution | Pins Used | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Link | 1920×1200 | 18+1 | Office work, web browsing |
| Dual-Link | 2560×1600 | 24+1 | Gaming, design, high-res video |
When buying a DVI cable, check if your monitor and graphics card both support dual-link. If only one side is single-link, your resolution will be limited.
What About the Analog-Only Option for DVI-A?
Still have old equipment lying around that uses analog video?
DVI-A is designed solely for analog signals and works with VGA displays, but it’s largely obsolete today.
When Would You Use DVI-A?
DVI-A is helpful when:
- You have an older CRT monitor that only accepts VGA.
- Your graphics card has a DVI-I output and you need to convert it to VGA.
| Connector | Signal Type | Compatibility | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| DVI-A | Analog Only | VGA via adapter | Mostly obsolete |
Why It's Less Common Today
With digital displays prevalent, DVI-A is rare. Modern monitors primarily use digital inputs like DVI-D, HDMI, or DisplayPort. DVI-I is more commonly used for analog compatibility than dedicated DVI-A ports.
How Do I Pick the Right DVI Cable?
Not sure which DVI cable you need for your setup?
For digital setups, use DVI-D. If you need analog compatibility, choose DVI-I. For high resolution, make sure it’s dual-link.
Cable Selection Guide
| Setup Type | Recommended Cable |
|---|---|
| Digital monitor + digital output | DVI-D single or dual |
| Analog monitor + analog output | DVI-I + VGA adapter |
| Mixed signals | DVI-I |
| High resolution display | Dual-Link (DVI-D/I) |
Choosing the wrong cable can result in no display signal, poor image quality, or even damaged connectors. Always match the signal type and resolution requirements.
DVI to HDMI and VGA
- DVI-D to HDMI: Works with a passive adapter (both are digital).
- DVI-I to VGA: Works with a passive adapter (both support analog).
- DVI-D to VGA: Needs an active converter, since signals aren’t compatible.
Double-check your monitor’s input ports before buying any cable or adapter.
Comparing DVI with VGA and HDMI
Do you still need DVI in a world of HDMI and DisplayPort?
DVI provides clearer visuals than VGA and is still useful where HDMI’s audio isn’t needed. HDMI, however, supports both video and audio, making it better for TVs and home theaters.
| Feature | VGA | DVI | HDMI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | Analog | Digital/Analog | Digital |
| Audio Support | No | No | Yes |
| Max Resolution | 1600×1200 | 2560×1600 | 4K+ |
| Adapter Ready | Yes | Yes | Yes |
If you’re connecting a computer to a monitor and don’t need audio, DVI still performs well. But for a TV or media player, HDMI is usually the better choice.
How Does DVI Stack Up Against Other Interfaces?
Is it time to retire DVI from your setup?
While DVI lacks modern features like audio and 8K support, it’s still dependable for clear video in professional and industrial settings.
| Feature | DVI | HDMI | DisplayPort |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Resolution | 2560×1600 | 4K+ | 8K+ |
| Audio Support | No | Yes | Yes |
| Adapter Flexibility | Moderate | High | High |
| Market Use | Industrial, PC | TVs, PCs | PCs, Pro Monitors |
DVI is slowly being phased out, but it still plays a role in legacy systems, industrial machinery, and custom display setups where only video is needed.
Conclusion
Knowing the difference between DVI-I and DVI-D helps you choose the right cable, avoid connection issues, and optimize your display’s performance.
Related Articles:
How Do Rise and Fall Times of the Enable Pin Affect Data and Display Quality in LCD1602 Modules?
How Does I2C for LCD Communication Work?
How Can a Serial In and Parallel Out Shift Register Simplify MCU to LCD Communication?
How Do You Handle Byte-Order (LSB vs. MSB First) in Page-Mode Writes?
How do timing controllers (TCON) synchronize image data in LCDs?
FAQ
Can I plug a DVI-I cable into a DVI-D port?
No, the extra analog pins on the DVI-I cable prevent it from fitting into a DVI-D port.
Is DVI better than VGA?
Yes, DVI provides better image quality because it can transmit digital signals, which are less prone to degradation.
Can DVI-D connect to HDMI?
Yes, with a passive adapter, since both support digital video signals.
Why won’t my DVI monitor display anything?
Yes, because DVI-D only carries digital signals and VGA only accepts analog.
Do I need an active adapter for DVI-D to VGA?
Knowing the difference between DVI-I and DVI-D helps you choose the right cable, avoid connection issues, and optimize your display’s performance.