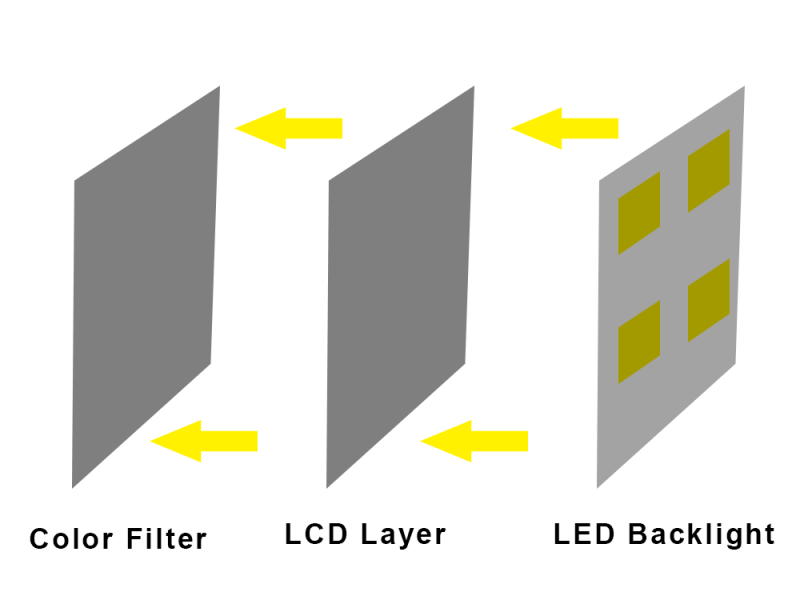
VCC delivers positive voltage, like 3.3V or 5V, to power logic or analog parts in an LCD display. VDD, often higher at 5V or 7V, feeds digital circuits such as the LCD driver ICs.
VSS sits at 0V and acts as the ground, connecting all power currents in the LCD panel. VEE, a negative voltage from -5V to -20V, adjusts contrast by biasing the liquid crystal layer.
These voltages each handle a unique job in an LCD module. Knowing them helps you design power supplies or fix display issues fast.
The differences shape how LCDs get power and stay stable. Later sections dive into their roles and circuit design impacts.
Comparative Analysis: How They Differ
| Power Input | Typical Role | Voltage Range | Common Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Powers logic/control circuits | 3.3V to 5V | Microcontroller interfaces, backlights |
| VDD | Powers digital driver ICs | 5V to 7V | Pixel switching in TFT LCDs |
| VSS | Ground reference | 0V | Circuit grounding, stability |
| VEE | Contrast adjustment | -5V to -20V | Character/passive matrix LCDs |
- VCC vs. VDD: Both are positive power supplies, but VCC is generally for logic or analog components, while VDD is for digital drivers. This distinction is crucial in TFT LCDs, where VDD might be 7V for drivers and VCC 5V for backlights, avoiding circuit overload if mixed up.
- VSS: Acts as the neutral reference, essential for all voltage measurements and circuit operation. Its role is non-negotiable, as incorrect grounding can disrupt the entire display.
- VEE: Unique as a negative voltage, VEE’s role is specific to contrast control in older or simpler LCD technologies, contrasting with the digital control methods in TFT LCDs.
What Does VCC Mean in an LCD Circuit?

VCC stands for “voltage common collector” and acts as the positive power supply, like 3.3V or 5V, for logic ICs or analog parts in an LCD. It powers components such as the microcontroller interface or backlight LED driver.
VCC plays a key role in keeping the LCD running smoothly by delivering a steady voltage to critical parts. A unique industry insight is that mismatched VCC levels can fry the LCD module or cause flickering displays if the voltage doesn’t align with the logic requirements.
- Voltage Range: Datasheets, like those for a 16×2 LCD module, often list a max voltage of 5V for VCC.
- Pairing with VSS: VCC works with VSS, the ground reference, to complete the circuit.
- Logic Match: The VCC voltage must match the LCD’s logic level, or you risk signal errors or hardware damage.
Where Does VCC Fit in an LCD’s Pin Layout?
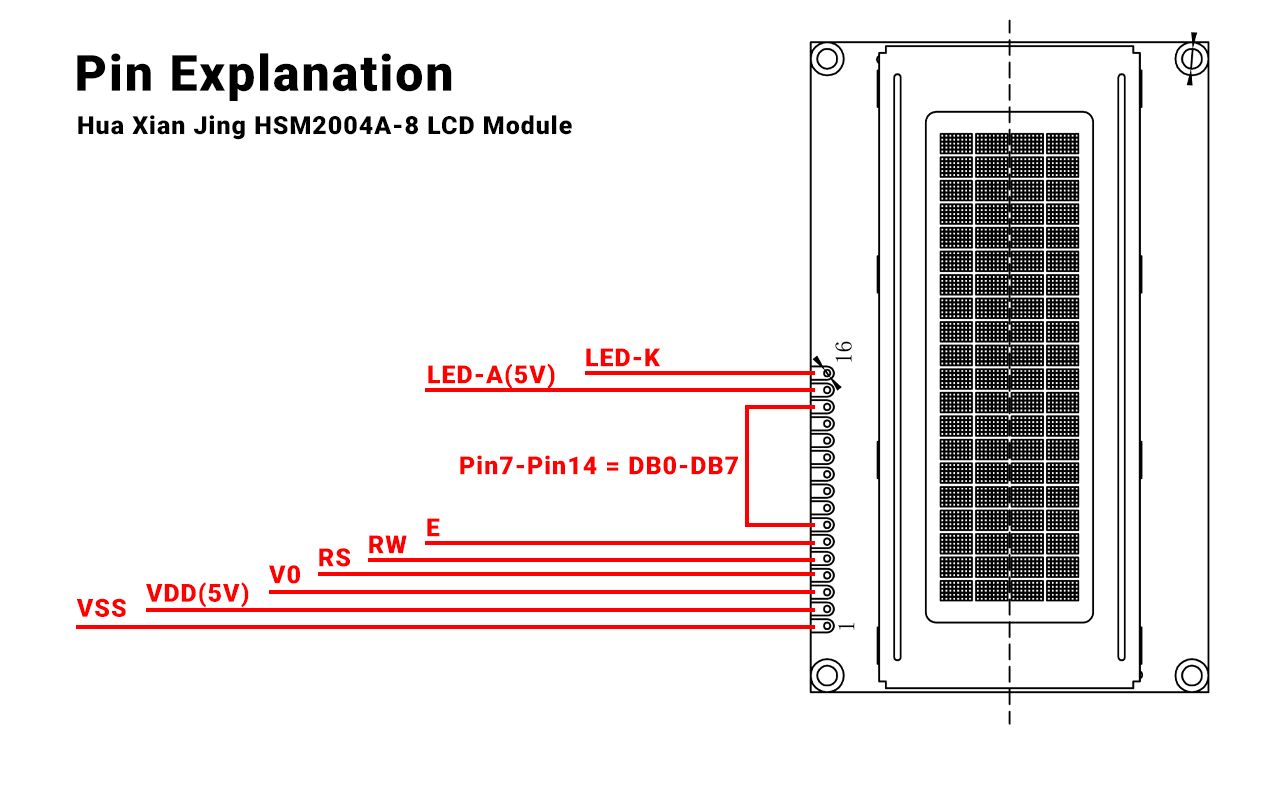
VCC connects to a specific pin—usually pin 2 on a 16×2 LCD—to supply power, while VSS ties to pin 1 for grounding.
This pin setup ensures the LCD gets power without confusion. It also helps users avoid wiring mistakes that could short the display.
- Pin Layout Example: In a 2×16 LCD, pin 1 is VSS (ground), pin 2 is VCC (5V or 3.3V), and pin 3 adjusts contrast.
- Check the datasheet for your LCD model, as some small LCDs shift VCC to pin 3 if extra features are added.
What Does VDD Do in an LCD Display?
VDD, or “voltage drain drain,” supplies positive power, like 5V or 7V, to digital circuits such as LCD driver ICs. It controls pixel switching in the LCD panel.
VDD keeps the digital parts of an LCD active by providing the right voltage for fast pixel changes. A key industry detail is that using a VDD lower than the driver’s spec can cause slow refresh rates or dim pixels.
- Voltage Range: VDD often hits 5V in basic LCDs but can reach 7V in TFT LCD designs.
- Driver Role: It powers the LCD driver ICs, flipping pixels on or off in the display.
- CMOS Link: VDD ties to MOSFET drain voltage, common in modern LCD display tech.
How Does VDD Differ from VCC in LCDs?
VDD powers digital drivers like TFT control logic, while VCC typically feeds logic ICs or analog parts.
This split matters because mixing them up can overload circuits. It also shows why some LCDs need both voltages for full operation.
- VDD vs VCC: VDD is CMOS-focused (digital), while VCC suits BJT or analog setups.
- A TFT LCD monitor might use 7V VDD for drivers and 5V VCC for backlights.
How Does VEE Affect LCD Contrast?
“voltage emitter emitter,” is a negative voltage, like -10V, that adjusts contrast in the LCD panel. It changes pixel opacity by biasing the liquid crystal layer.
VEE fine-tunes how dark or light pixels appear on an LCD screen. A lesser-known trick is that tweaking VEE slightly can fix washed-out displays without swapping parts.
- Voltage Range: VEE spans -5V to -20V, depending on the LCD display type.
- Contrast Role: It shifts the liquid crystal, key to how does a LCD screen work.
- Source: Often made by a charge pump or external supply in monochrome LCDs.
What Happens If VEE Voltage Is Too Low?
Low VEE weakens contrast, making the LCD screen look faded or unreadable.
This problem shows up when VEE can’t push the liquid crystal enough. Users often mistake it for a dead display instead of a voltage fix.
- Impact Data: A drop below -5V in a 16×2 LCD cuts contrast by half.
- Quick Fix: Boost VEE with a stable negative volts source to restore clarity.
How Do VCC, VDD, VSS, and VEE Work Together in an LCD?
VCC and VDD supply positive power, VSS provides 0V ground, and VEE delivers negative voltage for contrast in an LCD module. Each handles a specific role to keep the display running.
These voltages team up to power logic, drive pixels, stabilize signals, and adjust clarity in an LCD. A handy tip is that balancing them right prevents fuzzy screens or burnout in complex TFT LCD setups.
- Voltage Breakdown: VCC is 3.3V-5V for logic; VDD hits 5V-7V for drivers; VSS is 0V; VEE ranges -5V to -20V.
- Roles: VCC feeds the vcc pin, VDD powers LCD driver ICs, VSS grounds, and VEE tweaks how does an LCD screen work.
- Design Note: Use separate regulators for VCC, VDD, and VEE, tied to a shared VSS electronics ground.
How Can You Troubleshoot These Voltages in an LCD?
Check VCC and VDD with an LCD on a multimeter; low VEE muddies the LCD display definition.
Measuring keeps you from guessing what’s wrong with a blank screen. It’s a fast way to spot if VEE’s negative volts are off.
- Tool Use: Set your multimeter to display voltage; VCC/VDD should match the datasheet, VEE needs negative volts.
- Fault Fix: If VEE dips below -5V, contrast fades—adjust the supply to match lcd pin layout specs.
How Do VCC, VDD, VSS, and VEE Differ in an LCD?
VCC and VDD are positive voltages, with VDD often higher, while VSS is 0V ground, and VEE is negative for contrast. Each powers distinct LCD display parts.
These voltages split tasks to keep an LCD running smoothly. A handy insight is that mixing up VCC and VDD levels can overheat drivers, while VEE tweaks visibility.
- VCC: Positive, like 5V, for logic ICs in the LCD con.
- VDD: Higher positive, up to 7V, for LCD driver ICs.
- VSS: Fixed at 0V, the ground for all currents.
- VEE: Negative, -5V to -20V, adjusts LCD panel contrast.
Why Does Voltage Polarity Matter in LCDs?
Polarity sets each voltage’s job, ensuring the LCD screen works without shorts or glitches.
Wrong polarity fries circuits or blanks the display. It’s a detail users miss when swapping power supplies.
- Polarity Check: VCC and VDD stay positive, VSS is neutral, VEE goes negative.
- Real Risk: A flipped VEE voltage can lock pixels off in a TFT LCD.
What Roles Do VCC, VDD, VSS, and VEE Play in LCD Modules?
VCC powers logic at 5V, VDD drives digital circuits, VSS grounds at 0V, and VEE adjusts contrast. Each supports a specific LCD display function.
These voltages team up to make an LCD work right. A pro tip is that weak VSS grounding can mess up VEE’s contrast control, dulling the screen.
- VCC: Supplies 5V to the vcc pin for logic in the LCD pin layout.
- VDD: Feeds digital drivers, often 7V, per vdd meaning electronics.
- VSS: Holds 0V stability, key in vss electronics.
- VEE: Sets contrast with -10V, tied to how does an LCD screen work.
How Do These Roles Impact LCD Performance?
Each voltage’s job keeps the LCD panel clear, fast, and stable when done right.
Mess up one role, and pixels lag or fade. Users often skip checking VSS when contrast fails.
- Role Effect: Low VDD slows drivers; shaky VSS adds noise to the LCD con.
- Fix Insight: Test VEE voltage first if the small LCD looks off.
How Do VCC, VDD, VSS, and VEE Shape LCD Circuit Design?
VCC and VDD need separate regulators, VSS ties to 0V ground, and VEE requires a negative supply. These choices define the LCD display setup.
Designing for these voltages means balancing power needs without frying the LCD. A smart move is to use isolated regulators for VDD to avoid crosstalk with VCC.
- Power Setup: VCC at 5V and VDD at 7V often need distinct regulators.
- VSS Role: Shared 0V ground links all, per vss electronics.
- VEE Need: A -10V supply, separate from others, drives contrast.
How Can You Troubleshoot These Voltages in an LCD?
Check VCC and VDD with an LCD on a multimeter; VEE issues blur the LCD display definition.
Measuring voltages spots faults fast, like a low VDD starving drivers. Users miss VEE checks when screens fade.
- Test Method: Use a multimeter on the vcc pin (5V) and VDD (7V).
- Fault Sign: If VEE dips below -5V, contrast drops in the LCD panel.
How Do LED Drivers Power an LCD Backlight?
LED drivers use methods like PWM to control backlight brightness in an LCD display. They manage power separately from VCC or VDD inputs.
These drivers adjust light output without touching the LCD’s core power lines. A neat trick is pairing PWM with a high-frequency signal to cut flicker on TFT LCD screens.
- PWM Method: Pulses power at 100 Hz to 1 kHz to dim or brighten LEDs.
- Driver Role: Boosts efficiency, unlike direct VCC voltage feeds to backlights.
- Setup: Common in medium and small LCD module designs for precise control.
Why Don’t Backlight Drivers Rely on VCC or VDD?
Backlight drivers run on separate circuits to avoid overloading VCC or VDD logic power.
This keeps the display’s logic stable while lighting adjusts. Users often miss this split when diagnosing dim screens.
- Circuit Split: LEDs pull 5V to 12V, not tied to vcc vs vdd lines.
- Fix Tip: Check the driver IC, not VSS and VDD, for backlight faults.
Related Articles:
How to find a good LCD module manufacturer?
Difference between IPS TFT and TN TFT
All That There Is To Know About the Color Alphanumeric LCD Modules
How Should You Drive Backlight in an Embedded LCD Display?
How Are Embedded LCDs Used in Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) for Industrial Control Systems?
FAQ
What Voltage Should I Use for VCC and VDD in My LCD Module?
Check your LCD datasheet—VCC is typically 3.3V or 5V for logic circuits, while VDD might be 5V or higher (e.g., 7V) for the digital driver, depending on the module’s requirements. Incorrect voltages can damage the LCD panel or cause display failures.
How Do I Troubleshoot a Blank LCD Screen Related to Power Inputs?
Use a multimeter to measure VCC, VDD, and VEE against VSS (ground)—a missing or incorrect voltage (e.g., VEE too low) often causes a blank LCD display, indicating a power supply or connection issue.
Can I Use the Same Power Source for VCC and VDD in an LCD?
Yes, if their voltage requirements match (e.g., both 5V), but separate regulators are recommended if VDD exceeds VCC or if noise from the driver affects logic circuits in the LCD module.
Why Does My LCD Contrast Look Wrong Even With Correct VCC and VDD?
This is likely due to an improper VEE voltage—adjust the negative supply (e.g., -5V to -20V) as per the datasheet to fix contrast issues on your LCD screen.
What Happens If I Connect VSS Incorrectly in My LCD Circuit?
An incorrect VSS (ground) connection disrupts the reference for VCC, VDD, and VEE, leading to erratic LCD display means behavior or complete failure; ensure a solid ground path to avoid this.