LCD resolution refers to the number of pixels arranged across a display’s width and height, often written as “width x height” (e.g., 1920×1080 for Full HD). It directly impacts image sharpness, clarity, and the detail visible on the screen. The higher the pixel count, the more detailed and sharper the display appears.
Matching resolution appropriately to pixel density, screen size, and viewing distance is critical. For instance, a 27-inch monitor with 1080p resolution may look less sharp compared to a smaller screen with the same resolution due to reduced pixel density (PPI).
Users often encounter challenges with non-native resolution setups, which can cause blurring or scaling issues. These problems arise when hardware and software compatibility—such as graphics cards, display ports, and scaling technologies—are mismatched. Proper configurations can resolve these issues, ensuring displays perform at their best.
Understanding resolution also involves considering aspect ratios (e.g., 16:9), the relationship between width and height, which shapes the way content is displayed on the screen. For instance, a 1920×1080 resolution paired with a 16:9 aspect ratio offers a widescreen viewing experience ideal for movies or gaming.
When choosing an LCD resolution, it is essential to evaluate use cases, like gaming, office work, or creative tasks, since different applications prioritize sharpness, refresh rates, or text clarity.

What Are the Core Elements of LCD Resolution?
The core elements of LCD resolution include pixel count, aspect ratio, and pixel density (PPI). These aspects define the display quality, sharpness, and user perception of the screen.
The Role of Pixel Count in Image Quality
Pixel count forms the foundation of resolution. Higher pixel counts, such as 1920×1080 (Full HD) or 3840×2160 (4K UHD), result in sharper images and better clarity. A screen with a larger resolution can display more visual details, making it ideal for tasks like graphic design or watching high-definition content.
Key Formats:
- Standard HD: 1280×720
- Full HD: 1920×1080
- Quad HD (QHD): 2560×1440
- Ultra HD (4K): 3840×2160
How Does Aspect Ratio Shape the Viewing Experience?

Aspect ratio, such as 16:9, 4:3, or 21:9, determines the screen’s dimensions. It works in tandem with resolution to define how content fills the screen. For example, a 1920×1080 resolution in a 16:9 aspect ratio ensures widescreen viewing, perfect for movies or gaming.
Why Does Pixel Density (PPI) Matter?
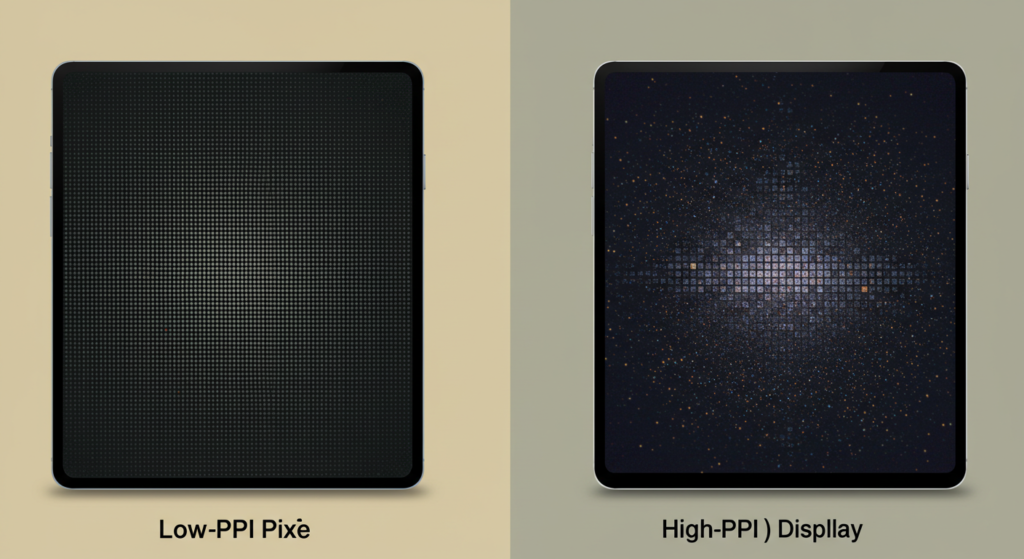
Pixel density, measured in pixels per inch (PPI), influences how sharp a display looks at different sizes and distances. For example, a 27-inch 1080p display may appear less sharp than a 4K display of the same size because the lower PPI spreads pixels across a larger surface. Viewers closer to the screen can notice individual pixels on displays with lower PPI.
What’s the Difference Between Resolution and Screen Size?
Resolution refers to pixel count, while screen size measures physical dimensions. A larger screen does not always mean better quality if the resolution remains unchanged. For example, a 32-inch screen with 1080p resolution will appear less sharp than a 24-inch screen with the same resolution(How Does Screen Size Affect Touch Accuracy?).
Key comparison:
| Screen Size | Resolution | PPI (Sharpness) |
|---|---|---|
| 24-inch | 1920×1080 | ~92 PPI |
| 32-inch | 1920×1080 | ~68 PPI |
How Do Hardware and Software Factors Affect LCD Resolution?
Hardware and software factors such as panel technology, resolution scaling, and signal processing directly influence a display’s sharpness, compatibility, and performance in varied setups.
Panel Technology's Role in Supporting Resolution
Modern LCD panels rely on liquid crystal alignment and transistor technology (e.g., TFT, IPS, VA) to support different resolutions. For example, IPS panels offer better color accuracy and support higher resolutions like 4K, while VA panels often excel in delivering better contrast ratios. Manufacturing limits, such as pixel defects and alignment precision, can cap the resolutions certain panel types achieve(How Do TN, IPS, and VA LCD Panels Affect Backlighting System Design?).
Key Panel Technologies:
- TFT (Thin-Film Transistor): Standard for most displays, reliable but limited in viewing angles.
- IPS (In-Plane Switching): Preferred for high-resolution desktop monitors due to wide color gamut support.
- VA (Vertical Alignment): Provides deep blacks but may face resolution and refresh rate trade-offs.
Why Do Resolution Scaling Challenges Arise?
Scaling issues typically occur when content is displayed at non-native resolutions, leading to blurred or distorted visuals. For example, a Steam Deck docked at 1080p on a native 720p screen can result in noticeable loss of sharpness. Multi-monitor setups with mismatched resolutions enhance this problem. Solutions like integer scaling or third-party software such as DisplayFusion help reduce blurring.
Examples:
- Docking a Steam Deck with a native 720p panel to output at 1080p may overburden the scaling algorithms, causing artifacts.
- Using different resolutions in multi-monitor setups (e.g., 1440p and 1080p monitors) leads to scaling mismatches.
Signal Processing and Compatibility for High-Resolution Outputs
Signal transmission standards, such as HDMI 2.1 or DisplayPort, play a critical role in maintaining compatibility with high resolutions like 4K or 8K. GPU performance, port bandwidth, and compression techniques such as DSC (Display Stream Compression) ensure smooth outputs while addressing hardware limitations like refresh rate caps. For instance, RTX GPUs paired with DSC-enabled monitors allow 8K displays to run at 60Hz with HDR enabled.
How Do Hardware Limitations Impact Refresh Rates at 4K?
Hardware limitations, such as GPU performance and port bandwidth, directly affect refresh rates at higher resolutions. For example, HDMI 2.0 limits refresh rates to 60Hz at 4K, whereas HDMI 2.1 supports 120Hz or higher.
Key Factors:
- Bandwidth: HDMI 2.0 supports up to 18Gbps, sufficient for 4K60, while HDMI 2.1 provides 48Gbps for higher refresh rates.
- Compression Techniques: DSC allows more data to pass through limited bandwidth without loss in quality, making it possible to achieve 4K120 or even 8K60.
How Do Human and Ergonomic Factors Influence Resolution Choices?
Human and ergonomic factors such as viewing distance, eye comfort, and task-specific needs significantly influence optimal resolution choices for various use cases.
How Does Viewing Distance Affect Resolution Perception?
The impact of resolution on sharpness changes with viewing distance. For instance, a desktop monitor viewed at close range benefits from higher resolutions, like 2560×1440, to maintain sharpness. On the other hand, TVs viewed from a greater distance appear adequately sharp even at lower resolutions, such as 1080p. Retina displays leverage this concept by ensuring pixel density is high enough that individual pixels are indistinguishable at typical viewing distances.
Key Examples:
- Desktop usage: Viewing from 18-24 inches benefits from resolutions such as QHD or 4K.
- TV usage: Watching from 6-10 feet away may only require 1080p for perceived sharpness.
Why Balancing Resolution and Eye Comfort Matters
Higher resolutions can enhance clarity but may strain the eyes if poorly balanced with refresh rates, screen size, or text clarity. For example, a 27-inch 4K monitor may make text appear too small, causing fatigue over prolonged use. Alternatively, lower resolutions like 1024×768 may reduce strain for office workers, as text and UI elements appear larger, promoting ergonomic comfort.
Potential Tradeoffs:
- High-PPI screens can cause “over-sharpness fatigue.”
- Low-refresh-rate displays at high resolutions may appear choppy, affecting comfort during scrolling or intense visual tasks.
Use Case-Specific Resolution Guidance
Optimal resolutions vary depending on the task or application:
- Gaming: Prioritize high refresh rates and low latency, e.g., 1440p at 144Hz.
- Creative Work: Focus on color accuracy, HDR, and sharpness, e.g., 4K with a wide color gamut.
- Office Productivity: Emphasize text legibility and moderate resolution, e.g., 1080p or 1440p.
How Does Screen Size Impact Ergonomic Comfort?
Larger screen sizes require matching resolutions to maintain clarity and avoid pixelation. For example, a 32-inch 1080p monitor may appear blurry due to reduced pixel density compared to a 24-inch screen with the same resolution.
Suggested Configurations:
| Screen Size | Optimal Resolution | PPI for Comfort |
|---|---|---|
| 24-inch | 1920×1080 (1080p) | ~92 PPI |
| 27-inch | 2560×1440 (QHD) | ~108 PPI |
| 32-inch | 3840×2160 (4K) | ~137 PPI |
How Can You Address Longevity and Durability Concerns with LCD Panels?
To prevent premature wear, it is crucial to reduce strain on the LCD’s components. Backlight failure occurs gradually, often caused by prolonged high brightness levels. Pixel degradation may show up as dead or stuck pixels over time, especially on older or heavily used screens.
Tips for Extending Longevity:
- Optimize Brightness: Keep brightness below 50% in most environments to reduce backlight strain.
- Enable Screen Savers: Prevent screen burn-in from static images by using dynamic screen savers or enabling sleep mode after periods of inactivity.
- Adjust Refresh Rate: Use standard refresh rates (60Hz or 75Hz) for non-gaming tasks to avoid excessive stress on the system.
How Does Viewing Distance Affect Resolution Perception?
LCD panel longevity and durability depend on factors like backlight lifespan, pixel degradation, and how the panel is maintained. Key practices such as optimizing brightness settings and using screen savers can extend the display’s life.
How to Maximize Panel Longevity?
To prevent premature wear, it is crucial to reduce strain on the LCD’s components. Backlight failure occurs gradually, often caused by prolonged high brightness levels. Pixel degradation may show up as dead or stuck pixels over time, especially on older or heavily used screens.
Tips for Extending Longevity:
- Optimize Brightness: Keep brightness below 50% in most environments to reduce backlight strain.
- Enable Screen Savers: Prevent screen burn-in from static images by using dynamic screen savers or enabling sleep mode after periods of inactivity.
- Adjust Refresh Rate: Use standard refresh rates (60Hz or 75Hz) for non-gaming tasks to avoid excessive stress on the system.
What Are Common Signs of Panel Degradation?
Signs like dimming backlights, discolored regions, or persistent image retention indicate panel aging. Degraded pixels may cause distortions, which can be alleviated by pixel fixing tools, although this solution applies primarily to stuck pixels rather than dead ones.
Real-life Example:
- A 5-year-old monitor with heavy daily use may experience a 20-30% brightness reduction, making it unsuitable for tasks requiring high color accuracy, such as photo editing.
How Can You Ensure Compatibility for Extended Use?
Ensuring compatibility requires using updated hardware and software standards that support the panel’s technology. For example, connecting a 4K monitor to an HDMI 1.4 port will limit its refresh rate to 30Hz, reducing its usability for modern workflows.
Best Practices:
- Use modern connection standards like HDMI 2.1 or DisplayPort 1.4 to fully utilize features such as HDR and higher refresh rates.
- Regularly update your graphics card drivers to avoid compatibility issues and maximize performance
FAQ
What Is Native Resolution, and Why Is It Important?
Native resolution refers to the exact number of pixels a display is designed to show optimally (e.g., 1920×1080 for Full HD). Using the native resolution ensures sharp images and avoids scaling issues like blurring.
How Does Pixel Density (PPI) Affect Visual Quality?
Pixel density, measured in pixels per inch (PPI), determines how sharp a display appears at different sizes. Higher PPI yields clearer images, especially on smaller screens or when viewed up close.
What Happens When a Screen Runs at a Non-Native Resolution?
Running a screen at a non-native resolution can cause blurring and distorted visuals due to mismatched scaling. This problem is common in setups like multi-monitor systems with different resolutions.
How Do Resolution and Screen Size Work Together?
Resolution determines pixel count, while screen size refers to physical dimensions. A larger screen with the same resolution as a smaller one may look less sharp due to lower pixel density.
Why Do High-Definition Displays Cause Eye Strain for Some Users?
High-definition displays can cause eye strain when text or elements appear too small, especially on high-PPI screens. Poorly balanced brightness or extended exposure can also contribute to discomfort.
Which Resolutions Are Best for Gaming vs. Office Work?
For gaming, prioritize resolutions like 1440p with high refresh rates (e.g., 144Hz). For office work, 1080p or 1440p provides clear text and easy readability without straining the eyes.
Can Adjusting Brightness Settings Extend the Life of a Display?
Yes, lowering brightness reduces strain on the backlight, which is a key factor in prolonging a screen’s lifespan. Avoid max brightness settings for extended durations.
Is It Possible to Fix Dead or Stuck Pixels?
Stuck pixels (always on) can sometimes be fixed using pixel-fixing apps or pressure tools. Dead pixels (always off), however, typically require panel replacement.
How Do HDMI and DisplayPort Affect High-Resolution Performance?
High-resolutions like 4K or 8K depend on port standards like HDMI 2.1 or DisplayPort 1.4 for sufficient bandwidth. Older standards often cap refresh rates, reducing performance.