Are you confused by display jargon like OLED and AMOLED? Many users find it challenging to discern if AMOLED is just a marketing buzzword or genuinely a superior display technology. Navigating display terminologies can indeed be overwhelming, especially when selecting components for high-performance electronic devices.
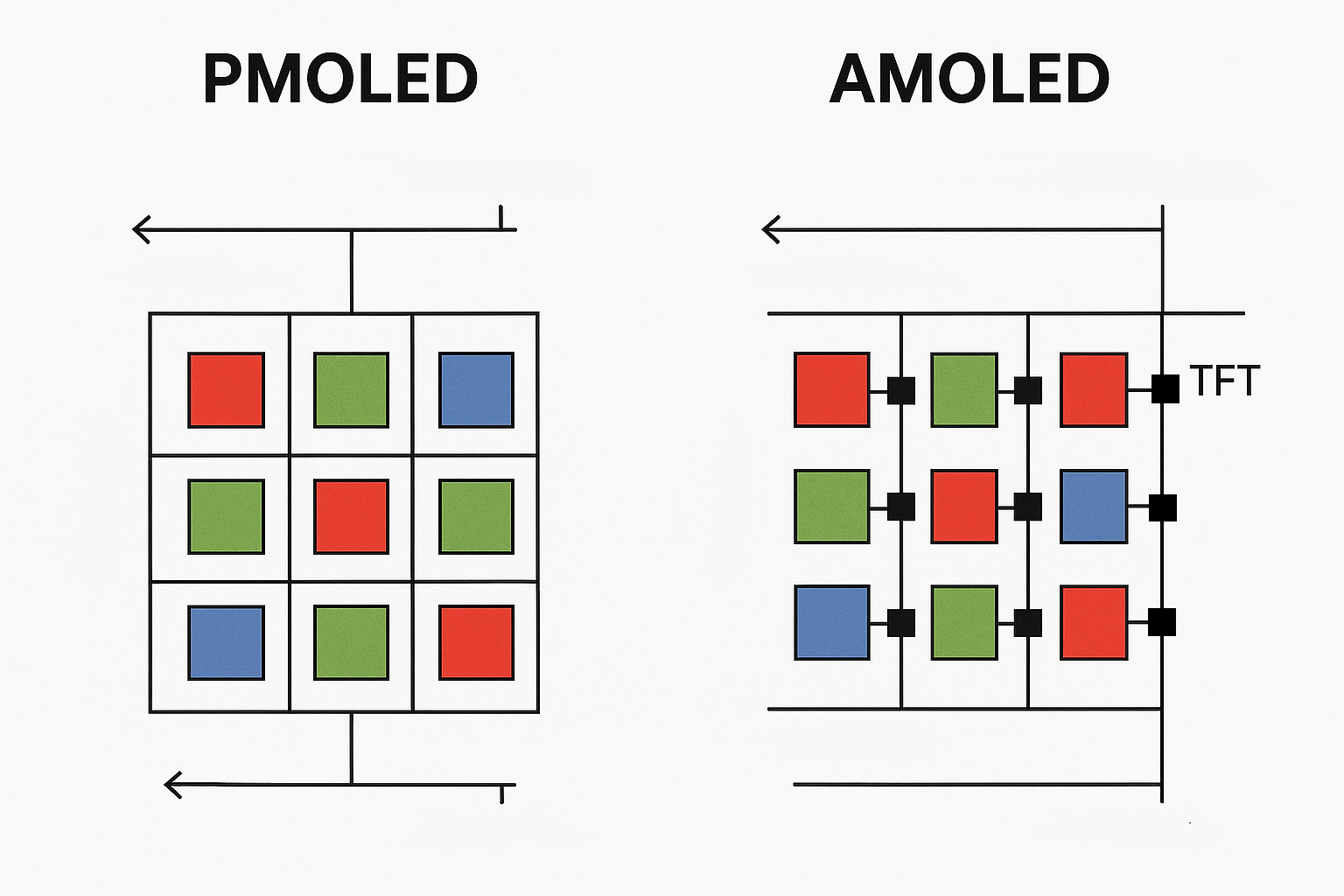
The main difference is that AMOLED incorporates an active matrix using thin-film transistors (TFTs) for precise, individual pixel control, offering significantly faster response times, superior power efficiency, improved touch integration, enhanced resolution scalability, greater uniformity, better color consistency, and higher peak brightness compared to standard OLED displays.
Recently, while sourcing displays for a client’s premium electronic products, I encountered numerous misconceptions surrounding OLED and AMOLED. Let’s systematically address these misunderstandings to enable informed decision-making and optimal technology selection.
What Are the Technical Differences Between OLED and AMOLED?
Curious about what technically distinguishes AMOLED from traditional OLED?
OLED displays utilize organic materials that emit light upon electric current application, generally driven by passive matrix technology. Conversely, AMOLED leverages active matrix technology employing TFTs for individual pixel control, substantially enhancing response speed, resolution, uniformity, brightness precision, color accuracy, and energy efficiency.
What Are the Technical Differences Between OLED and AMOLED?
OLED screens initially relied on passive matrix configurations (PMOLED), limiting their capacity for high resolution, uniform brightness, swift responsiveness, and precise control. AMOLED’s active matrix approach addresses these limitations effectively:
| Feature | OLED (Passive Matrix) | AMOLED (Active Matrix) |
|---|---|---|
| Pixel Control | Row & Column | Individual Pixel |
| Response Time | Slower | Faster |
| Power Efficiency | Moderate | High |
| Integration | Limited | Advanced Touch & Flexibility |
| Resolution Scaling | Limited | Excellent |
| Uniformity | Lower | Superior |
| Brightness Control | Less Precise | Highly Precise |
| Color Consistency | Moderate | Excellent |
| Refresh Rate | Limited | High |
| Scalability | Restricted | Excellent |
AMOLED’s integrated TFTs facilitate quicker pixel response times, crucial for smooth, fluid animations and dynamic content such as gaming, videos, and interactive applications, minimizing ghosting and enhancing visual quality.
What Practical Benefits Does AMOLED Have Over OLED?
Wondering if AMOLED justifies its higher cost compared to traditional OLED?
AMOLED technology offers faster refresh rates, improved battery efficiency—particularly noticeable in darker-themed displays—superior touch responsiveness, thinner and lighter form factors, enhanced image and color quality, and the capability to produce flexible and foldable screens, making it ideal for smartphones, wearables, automotive displays, and high-end medical equipment.
Advantages
The superior control over pixels that AMOLED technology provides has significant practical implications in modern, high-performance devices:
- Extended Battery Life: AMOLED screens completely shut off pixels when displaying true black, greatly extending battery life, especially beneficial when using dark modes and night settings.
- Enhanced Touch Integration: AMOLED’s integrated touch capabilities offer superior responsiveness and accuracy, exemplified by technologies such as Samsung’s renowned Super AMOLED.
- Innovative Device Designs: Supports flexible substrates (POLED) for foldable smartphones, curved wearable devices, and next-generation automotive infotainment systems.
- Higher Resolution and Screen Sizes: Efficiently scales up to large screens with ultra-high resolutions without sacrificing image sharpness, ideal for tablets and high-end smartphones.
- Reduced Device Weight and Thickness: Enables thinner and lighter displays, essential for achieving premium, sleek product designs.
- Superior Brightness and Outdoor Visibility: Provides enhanced brightness control and performance, improving visibility across various lighting conditions.
- Improved Durability: Offers greater flexibility and resistance to cracking compared to traditional rigid displays.
How Does Image Quality Compare Between OLED and AMOLED?

Are AMOLED screens visually superior to traditional OLED?
OLED and AMOLED both offer outstanding contrast, deep blacks, and vibrant colors, due to their self-emissive pixels. AMOLED, however, typically outperforms in motion handling, brightness uniformity, color accuracy, viewing angles, and overall viewing comfort, particularly during prolonged usage.
| Aspect | OLED (PMOLED) | AMOLED |
|---|---|---|
| Contrast Ratio | Infinite (true blacks) | Infinite (true blacks) |
| Color Accuracy | High, depends on calibration | High, depends on calibration |
| Motion Clarity | Moderate, possible ghosting | Excellent, reduced ghosting |
| Brightness | Good, panel-dependent | Often higher, panel-dependent |
Image Quality
Both technologies achieve exceptional contrast ratios through individually lit pixels. AMOLED’s active matrix enables faster pixel response, providing smoother animations and superior handling of dynamic visual content:
- AMOLED: Outstanding motion clarity, higher peak brightness, superior brightness uniformity, more accurate colors, reduced motion blur, and greater visual comfort.
- OLED (Passive Matrix): Potential for ghosting at higher speeds, inconsistent brightness across large panels, slower response times affecting visual comfort, limited brightness, and relatively lower color accuracy.
What Are the Differences Between OLED, AMOLED, and Related Technologies?
Tech terms like Super AMOLED or QLED confuse buyers. I’ve clarified these for clients. Let’s sort out the terminology.
Super AMOLED is AMOLED with integrated touch layers. POLED uses plastic substrates. QLED is a separate LCD-based technology. PMOLED is simpler, low-resolution OLED.
Navigating Display Terminology
The display world is full of acronyms. I often explain these to clients sourcing components. Here’s a breakdown:
1. Super AMOLED
Super AMOLED, developed by Samsung, is AMOLED with a built-in touch layer. This reduces thickness and improves sunlight visibility. I’ve seen Super AMOLED in premium smartphones, offering vibrant, responsive displays.
2. POLED
POLED (Plastic OLED) is AMOLED with a plastic substrate instead of glass. It’s flexible, used in curved or foldable screens. I’ve supplied POLED modules for innovative wearable designs.
3. PMOLED
PMOLED uses a passive matrix, limiting it to small, low-resolution displays like fitness trackers. Its simplicity suits basic applications, but it can’t scale like AMOLED.
4. QLED
QLED, unlike OLED or AMOLED, is not self-emissive. It’s an LCD with quantum dots for better color. I tell clients QLED is brighter but lacks OLED’s true blacks.
summary table:
| Technology | Base Type | Key Feature | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| PMOLED | OLED | Passive matrix, simple | Small displays, wearables |
| AMOLED | OLED | Active matrix, high-res | Smartphones, TVs |
| Super AMOLED | AMOLED | Integrated touch layer | Premium smartphones |
| POLED | AMOLED | Plastic substrate, flexible | Foldable phones, wearables |
| QLED | LCD | Quantum dots, high brightness | TVs, monitors |
What Are the Drawbacks of OLED and AMOLED?

Curious about potential disadvantages of AMOLED and OLED screens?
Both technologies can experience burn-in from prolonged static imagery. AMOLED specifically may suffer shorter pixel lifespans due to increased driving currents, complex manufacturing processes, higher costs, and potential user discomfort from PWM-induced flickering.
| Feature | OLED/AMOLED | IPS LCD |
|---|---|---|
| Black Levels | True black, infinite contrast | Grayish blacks, lower contrast |
| Brightness | Good, panel-dependent | Higher, better for outdoors |
| Burn-in Risk | Moderate risk | None |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Viewing Angles | Excellent | Very good |
Potential Issues
Despite AMOLED’s superior performance, consider these factors:
- Burn-in Risks: Static images left onscreen for extended periods may cause permanent ghosting on AMOLED displays.
- Shorter Pixel Lifespan: AMOLED pixels—particularly blue subpixels—may degrade quicker from high brightness and intense usage.
- Higher Manufacturing Costs: Advanced production techniques and intricate designs elevate AMOLED’s manufacturing costs and consumer prices.
- PWM Dimming: AMOLED screens frequently use pulse-width modulation for brightness adjustment, which can cause discomfort, eye strain, or headaches for sensitive individuals.
- Vulnerability to Physical Damage: AMOLED’s complexity and thin form factor may increase susceptibility to impact or damage compared to traditional LCD screens.
Conclusion
OLED is the base technology; AMOLED enhances it with active matrix control. AMOLED offers faster responses, efficiency, and flexibility, ideal for modern devices.
Related Articles:
What EMI/EMC Rules Must Automotive LCD Displays Follow?
How Is Hot-Swapping Handled in Modern LCD Controller Boards?
How Do You Choose the Best Microcontroller or Processor for Your LCD Module Project?
How is CAN or LIN Bus Integration Handled with LCD Modules?
What Is the Difference Between Capacitive and Resistive Touch Screens?
FAQ
Is Super AMOLED different from AMOLED?
Super AMOLED integrates touch sensors, reducing thickness and improving visibility. It’s an enhanced AMOLED, commonly used in premium smartphones.
What is PMOLED, and how does it differ?
PMOLED uses a passive matrix, suited for small, low-resolution displays. AMOLED’s active matrix supports larger, high-resolution screens with faster performance.
Does AMOLED have better colors than OLED?
No, both use the same organic compounds, offering identical color and contrast. AMOLED’s active matrix improves motion clarity, not color quality.
Is QLED related to OLED or AMOLED?
QLED is an LCD-based technology with quantum dots, not self-emissive like OLED/AMOLED. It’s brighter but lacks true blacks.
Why might AMOLED flicker?
AMOLED often uses PWM dimming, which can cause flicker at low brightness. Some users notice this, but it varies by panel design.